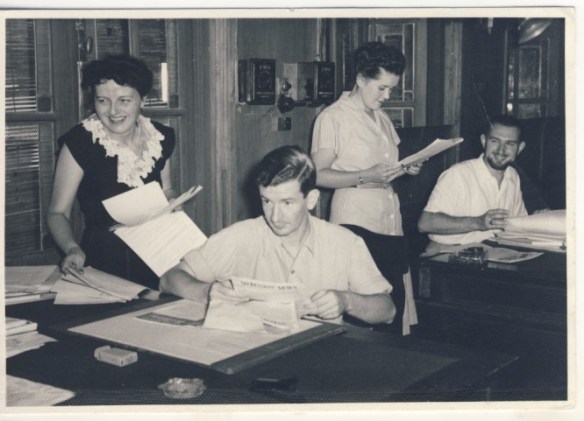
































In September 2021, I posted Joe Majerle’s analysis of the Albertina crash here for everyone to read. He has revised his analysis, dated 7 June 2023, “based on information found in the personal files of the late Bo Virving, Chief Engineer of Transair Sweden, A.B., made available by his son, Bjorn Virving.” I am sharing this in connection to the testimony of Sgt. Harold Julien – and, also, to stress the importance of Bo Virving’s documents and observations. From Majerle’s analysis, pages 25-26:
“THE PRECIPITATING EVENT“
“To my observation, in the study of aircraft accidents throughout the course of my life, there is almost always a precipitating event that sets off a chain of actions, reactions, counteractions, etc. that result in the crashed aircraft somewhere on the surface of earth. In this case, it is known from Annex II that the captain communicated to Ndola tower that all was well and within minutes the aircraft was being incinerated with its own wing fuel and that fifteen of the sixteen occupants’ lives has ended, and that the last would succumb in less than a week. That person, Sgt. [Harold] Julien, was the only eyewitness to the crash.
“To my experience, eyewitness testimony is considered evidence in a court of law, at least in this country. I am unfamiliar with Rhodesian law in the 1960’s, but in the USA in the 1960’s Sgt. Julien’s statements would have been considered evidence in a crash investigation. Since there is no other actual evidence to the contrary, and testimony of ground observers about the airport over-flight and entry to the instrument approach procedure are insufficiently conclusive to determine externally what the precipitating event was, it seems logical to me that Sgt. Julien’s statements, as brief as they are, are the only thing that can be considered as evidence in a search for the cause of the chain of events leading to the crash.
“In the UN Commission report, par. 129., Senior Inspector Allen testified to the UN Commission that he spoke with Sgt. Julien and asked him three questions; 1.”What happened? He said: ‘It blew up’.” 2.”Was this over the runway? And he said ‘yes’. 3.”What happened then? And he replied: ‘There was great speed – great speed’.”
“It blew up–“
“–over the runway”
“I have read all three of these reports several times and still don’t understand the reluctance of the investigators, including the UN and the Swedish observers, to not make those six words the central point, the number one item on the list of where to begin to find the truth about what happened. Especially from the standpoint of determining whether or not there is fault to be assigned to the flight crew.
“Assuming Sgt. Julien was belted into any seat in the forward cabin, looking out the side window on whichever side he was sitting on, he may or may not have had a view of the lighted runway and the town of Ndola but it is likely that the captain would have informed the passengers that they had arrived overhead Ndola and would be setting up to land there. It would have been the last thing he could identify location-wise and anywhere in that vicinity for him would be “over the runway”. I don’t know if Inspector Allen was deliberately trying to trip him up or why he asked him if it was over the runway when he knew that the aircraft had overflown the runway and not blown up there, but, it seems to me, it was an unusual question to ask a person in Sgt. Julien’s condition. What I am getting at here is that Sgt. Julien knew where the runway was and that the aircraft had blown up. They sound like lucid answers to me, and not as though he was thinking about horses or submarines, for example.
“In my view, in light of all the data and evidence of all of the pages of all the reports and the information displayed in all of the images of all the photographs in the UN file, the only thing I can see that qualifies as a precipitating event is Sgt. Julien’s: “It blew up”.
“And he was the only one left that was there when it happened.”
As I pointed out in part two of this series, Hugo Blandori was a “retired” FBI agent, turned private investigator, who was hired by the UN as a consultant to this investigation. It is extremely upsetting to me that an FBI agent was involved, not only because of the racist history of that organization, but because of the role the FBI played during the McCarthy witch-hunt on United Nations staff members in 1953. Trygve Lie, the first UN Secretary-General, gave the FBI carte blanche of headquarters “for the convenience”, and it was his successor Dag Hammarskjold who protected his staff and kicked out the FBI by November 1953. Within every organization, including the UN, there have always been members who are actively working against the good that that organization is trying to achieve, and that is how I believe Hugo Blandori got the job of consultant. This is also how Dr. Max Frei-Sulzer – a Swiss police official that believed Hitler’s diaries were real – was appointed by the UN commission to examine the wreckage of the Secretary-General’s plane, and “who reported that there were no bullet holes in the plane and no evidence of explosives that would have been needed for a time bomb or other means of sabotaging the plane”. In my view, the contributions of Blandori and Frei-Sulzer are not just highly suspect, they discredit the investigation – I believe intentionally so!
This is why I am grateful for Bo Virving (and his son, Bjorn!), who was the smartest man on the scene in Ndola – an honest man – who saved important documents from the investigation, convinced that the crash was not an accident and that African witnesses testimony were deliberately ignored.
From Virving’s documents, “Memoranda submitted by Mr. Hugo Blandori, Consultant”, 21 February 1962, pages 8-9:
“Mr. Virving, in his appearance before the Commission, presented a theory wherein he claimed that aircraft SE-BDY had been shot down or forced down by a plane above it. He based his theory primarily on the statements of African witnesses that had been interviewed in Ndola. I talked with Mr. Virving at length after his appearance before the Commission, but he could not elaborate nor could he suggest any ways and means of confirming his beliefs. He made it known that the Rhodesian authorities had sought to suppress those witnesses whose testimonies were embarrassing to the Rhodesians and to emphasize those who vindicated their stand.
“Virving stated that he was limited in his movements and was unable to undertake an independent investigation to further his theory.”
From pages 9-10, Blandori writes this about the African witnesses:
“Concerning African witnesses, I wish to point out that it is most difficult to distinguish from their testimony what is truth and what is fiction or imagination. There were so many inconsistencies and discrepancies in their stories that to have believed them would refute the testimony of other witnesses who are generally reliable.
[…]
“As a consequence, I am of the opinion that the testimony of the African witnesses to the effect that they saw one or more small crafts flying along with SE-BDY just prior to its crash, has to be accepted with a grain of salt.”
From “Report of the UN Commission of Investigation, 1962” p.46, par.143:
“Mr. Virving, a Transair official, put before the Commission a theory that SE-BDY might have been attacked and shot down by a plane armed with rockets. This theory was based in part on an analysis of the statements of various witnesses concerning their observations of planes and of flashes in the sky. No substantial evidence was submitted in support of this theory and the Commission is of the opinion that most of the phenomena referred to by Mr. Virving are susceptible of other and more logical explanations. The Commission also consulted rocket experts with ONUC who expressed considerable doubt concerning the possibility of such an attack. Finally, as already noted, no signs of a pre-crash explosion or traces of a rocket were found in the wreckage.”
From Susan Williams’ “Who Killed Hammarskjold?”, 2016 edition, chapter 7, p. 99:
“All these [African] witnesses were challenged by the Federal examiner. Afterwards, Bo Virving followed [Dickson] Buleni and [Davidson] Simango from the court and interviewed them privately about what they had seen. They repeated their claim that they had seen two aircraft and not just one but were reluctant to talk too much to Virving, as they were being observed by a white police officer. According to Virving, their answers were reliable and tallied exactly with his own technical calculations.”

Back in January 2014, I wrote here that I was convinced that the Albertina was shot down by Fouga Magisters. I am still convinced it was shot down, but I was wrong to believe it was a Fouga. I was misdirected by all the reports in the newspapers I was looking at, and I think that was the point – that these reports on Fougas were a red herring in the press. Bo Virving’s observations led him to believe that the Albertina was shot down by a Dove, and his theory rings true for me. From “Who Killed Hammarskjold?”, chapter 15, pages 185-187:
“Bo Virving had gathered ‘overwhelming evidence’, believed [George Ivan] Smith, that Hammarskjold’s plane was ‘forced down and crashed as a result of actions from an unidentified aircraft’. This evidence was carefully explored in a series of programmes about Hammarskjold which were produced by Gunnar Mollerstedt and shown on Swedish television. Mollerstedt had spent a year gathering material–including the interviews with Timothy Jiranda Kankasa and Dickson Buleni.
“Virving stated that there were five Doves in service in the Katangese air force in September 1961 at Kolwezi and Jadotville airports. They could stay airborne for three or four hours and their speed could match that of Hammarskjold’s DC6 in level flight; and in a dive from above they could increase their speed. It would be possible for the crew of the Dove to drop a small explosive device on to an aircraft below, then pull out of the dive. Virving had developed this theory about a Dove because on the day that Hammarskjold’s body was flown out to Sweden, he had seen a Dove at Ndola airport and discovered that it had a hole in its floor, which was apparently used for aerial photography. A man could lie there, he realized, telling the pilot ‘right, left, up, down’ and at a given moment let fall a small projectile.
“The theory that a Dove could be used in this way was later confirmed by Mercenary Commander, the memoir of the mercenary Jerry Puren–which was published six years after Mollerstedt’s programme. With evident pride, Puren describes in this book his technique of dropping bombs through a hole in the floor of a Dove aeroplane, by means of a rack system rigged along the fuselage. The racks were fitted to take bombs of 12.5 kg, which were despatched one at a time through the hatch in the floor when a lever was pulled. A bombing crew consisted of a pilot, a bomb aimer and a bombardier; usually Puren flew on these bombing missions with his friend Max Glasspole, the gum-chewing Canadian pilot, or the Hungarian pilot Sandor Gurkitz–both of whom were at Ndola airport on 17-18 September 1961, when he arrived that afternoon from South Africa. According to Puren, 12.5 kg bombs were turned out by Union Miniere workshops by the thousand; each had a contact fuse in the tail section which unwound and armed the bomb when lobbed from the aircraft.
“The Rhodesian Commission of Inquiry Report acknowledged that a Dove with a bombing capacity was found in September 1961 at Ndola–but after the crash. ‘One De Havilland Dove belonging to the Katanga Government,’ it stated, ‘was after the 18th September armed by removing a door and placing a machine gun on the floor to fire through the opening.’ The Dove had not, it stated, been at Ndola on the day of the crash, but elsewhere: ‘On 17th September this and possibly another were in the hands of the United Nations at Elisabethville. Three Doves were then in the Republic of South Africa undergoing examination.'”
[…]
“Virving’s suspicions about the use of a Dove against the Albertina were heightened when he went to Elisabethville in 1962 and found that the Katangese Doves had disappeared during the August 1961 UN action to expel mercenaries [Operation Rum Punch]. Significantly, their logbooks had been left behind. Then Virving found the Pretoria workshop where the Doves would normally have been serviced and sought information ‘for historical purposes’; but after two years’ wait he was told that no information could be given.”
Jerry Puren was one of the 79 mercenaries working for Katanga that uncle Vlado had arrested during Operation Rum Punch–he was also in the bar at Ndola airport the night of 17-18 September 1961, waiting for Hammarskjold’s plane to arrive. I believe that he was one of the men flying the Dove that shot down the Albertina. It wasn’t just glory he was after, it was personal revenge against Vlado and the UN for arresting him. From page 225-226 of “Who Killed Hammarskjold?”:
“[…]Puren’s behaviour at Ndola airport that evening seems totally out of character: for even though ‘excitement ran high, history was unfolding, and we were right on the spot,’ as he himself writes, he and fellow mercenary pilot Glasspole (who was also at Ndola airport) decided to have an early night:
Shortly after 22h00 there was a rustle of excitement among the chilled gathering. Several people claimed they had heard the sound of an aircraft’s engine, others said they saw lights disappearing low in the west. We saw nothing. Eventually Glasspole and I looked at each other, shrugged our shoulders and returned to our welcoming beds at the Savoy Hotel.
“This is a very different Jerry Puren from the man of action described in the rest of his memoir: who fearlessly, for example, escaped the UN after his capture during Rumpunch, disguised as a priest.”
[…]
“Puren’s and Glasspole’s unlikely early night at Ndola does make me wonder about the Dove found by Bo Virving at Ndola airport the following day–with a hole in the bottom, through which Puren and Glasspole had become adept at dropping bombs on to Baluba villages. Furthermore, Puren was rewarded by Tshombe just a few days after this episode, by being made Chief of Operations of the Katangese Air Force, at an impromptu parade.
“One intriguing aspect of Puren’s mercenary career is that he later became involved in the failed Seychelles invasion in 1981, with which SAIMR was apparently associated.”
Lastly, in connection to mercenaries and Doves, this brief interview with author and journalist Maurin Picard:
I am a bit slow in posting the latest Hammarskjold investigation news, but here is the link to the 2022 UN report from Judge Othman, which was released at the beginning of November. Many thanks to Judge Othman, and to all “individual researchers and non-State entities” who have been responsible for providing “almost all new information generated between 2020 and 2022”. From page 9 of the report: “Despite the decrease in the amount of information identified by Member States, the amount and quality of new information provided by individuals and non-State entities highlights that additional information is highly likely to exist in Key Member States’ records and archives.” As a reminder, those “Key Member States” are South Africa, United Kingdom, and the United States. From page 34 of the report: “…a small number of Member States, which have been identified as being almost certain to hold relevant information, appear to have been the least willing to provide further disclosure.”
From the Fabry archive, I have recently discovered a new stack of international newspapers from the 19th-27th of September 1961. Here are two papers from London, both from the 19th of September:











This is the full interview of Monique Cégel (now Madame Rime) sent to me in May 2020 by Maurin Picard, journalist and author of “Ils Ont Tue Monsieur H”; a portion of this interview was published here back in September 2020, “Vlado and the Mercenaries: Operation Rum Punch“, but I feel the whole interview deserves attention.
You can hear more interviews with Madame Rime about her experiences in the Congo working for the United Nations, with journalist David Glaser, reporter at GeneveMonde.ch.
Many thanks to Madame Rime, and to Maurin Picard for this interview and supporting the Hammarskjold investigation, and to David Glaser for promoting this blog and the life of Vlado Fabry – merci beaucoup to all who have contributed to this site!
Interview with Monique Rime Cégel
3 May 2020
Switzerland
Summary
– Monique Cégel, 83, was Vladimir Fabry’s secretary in Leopoldville in 1961
– She worked at the Hotel Le Royal between December 1960 and January 1962
– She knew Alice Lalande and Harold Julien very well
– She was working extra hours on 17 September 1961
– She typed Dag Hammarskjöld’s last message to Paul Henri Spaak, requesting Belgium to stop « van Riessenghem »
– She remembers there were serious doubts about UN communications being intercepted
– Vladimir Fabry did most of the research regarding Katanga mercenaries during the summer of 1961
– She remembers Dag Hammarskjöld’s collaborators tried to deter him from flying unescorted
– She does not think Sture Linnér was intended to fly along, as he had to stay in Leopoldville to liaise and work proper transmissions
– She flew to Ndola with Mahmoud Khiary on 19 September 1961 to type the ceasefire agreement with Moise Tshombe
– She saw the crash site right above her plane window prior to landing and was horrified
– She recalls smoldering debris and the « long line » of burnt forest
– She found a very hostile atmosphere in Northern Rhodesia
– She met a very disdainful Lord Alport
– She was not allowed to join Mahmoud Khiary at the hospital to visit Harold Julien
* * *
I was Vladimir Fabry’s secretary, at the Hotel Le Royal, Leopoldville (Congo).
I worked there for the UN mission in Congo from December 1960 to January 1962, as secretary detached from the Atomic Agency (IAEA) in Vienna.
I kept working for the UN in Geneva until 1976, mostly through freelancing contracts. Then my husband and I moved to the city of Bulle.
I met my husband in 1961 in Congo!
He was a representative for major Swiss companies of the time, including Schindler and Vega, and was selling chemical products to the university of Lovanium.
I became a Swiss citizen, after getting married with him.
I was French (and I still am), and was born in Paris.
* Sunday 17 September 1961
At the Hotel Le Royal, we had an office adjacent to the one occupied by Sture Linnér.
On the day Dag Hammarskjöld took off from Leopoldville, that Sunday, I was not supposed to work.
But, as Fabry’s secretary, and since he only worked with me, they sent some military staff in a Jeep to pick me up and bring me back to Le Royal.
They found me sitting at a cafe terrace, since I believe they always kept an eye on us for safety.
I went back to my office and worked all afternoon, until the plane departed.
* Vladimir Fabry
That day, when I arrived at my office, Vladimir Fabry immediately requested to dictate some telegrams. I spent the whole afternoon doing that: typing messages, then bringing them to the « Chiffre » for them to be coded accordingly with the recipient’s identity.
By the time I was finished, they were getting ready to leave for the airport.
Before leaving, Vladimir Fabry was so thrilled.
Happy as a kid who was just offered a new toy.
Albeit a very reserved character, he was practically jumping on his feet.
He came into my office and said excitingly:
« Monique, I am leaving with the Secretary-General! I am trusting you with my car keys! »
He had to be very happy, for he would never have done such a thing otherwise.
His car was an official UN vehicle.
He told me I could use all the time during his absence.
God knows Leopoldville is a very large town, with great distances between the various locations.
I used the car until, of course, I handed it back to the UN, since Fabry never returned.
I remember seeing their cars leaving Le Royal in convoy.
I went through these events with an innocent mind as I could only partially grasp what was going.
I would mostly type messages dictated by Fabry, messages that were generally meant for New York.
The last message I typed from them was dictated by M. Hammarskjöld himself. The recipient was Paul-Henri Spaak.
(nota: the Belgian Foreign Minister)
But I cannot remember its content (nota: requesting Belgian assistance to put an end to the criminal deeds of a mercenary pilot named « van Riessenghem »).
I was so intimidated that I must have skipped two or three words he dictated.
I had never met Hammarskjöld and I was so young then (nota : she was 24).
I saw Dag Hammarskjöld every day between 13 and 17 September 1961, since he occupied Sture Linnér’s office.
* Can you recall Hammarskjöld’s state of mind?
I remember he was not very agreeable. He seemed really sad, not at all in a communicative mood. « You do this, this has to be done ». We were in the midst of a serious crisis with Katanga, obviously.
* Were there long sleepless nights at Le Royal?
I did not spend those ones with them, but I had a similar experience during the previous months. When you are assigned to someone high ranking, you did not count your days and your nights. With all the crises we went through, there were many sleepless nights at Le Royal.
* Harold Julien
I knew Harold Julien very well, as he was the Chief Security Officer in Leopoldville. Being M. Fabry’s secretary, I was granted the use of a car.
This in turn created some serious trouble, because we were taken hostage with a Swiss colleague of mine by Mobutu’s troops for 24 hours. The time was around end January or early February 1961.
They had spotted my car, I believe, due to the UN flags on it, and surrounded our house with two small armoured cars. There were rumors that the UN was bent on disarming the Congolese National Army. And we had been poorly inspired to move in a house across the street from Mobutu’s barracks along the river – a magnificent location, it was indeed.
Then the witchhunt began against all UN staff.
This is the only time in my life I was really scared.
I called the French embassy asking for their help, as I was a French citizen. Their answer was very … kind: « you work for the UN, hence you are no longer considered as a French citizen for us. There is nothing we can do for you ».
Since my colleague was Swiss, she called the Swiss embassy and they immediately answered. « Yes of course, we will come and rescue you ».
They arranged for a motorized convoy of Swiss people, with friends and colleagues of my future husband, led by the Red Cross delegate M. Olivet, who was killed another day.
(nota: Georges Olivet, 34, was killed in an ambulance on 12 December 1961, amidst heavy fighting in Elisabethville, Katanga)
They parlayed with Mobutu’s soldiers, who pretty quickly removed their blockade and let us go free.
* Saturday 16 September, Lord Lansdowne meets Dag Hammarskjöld. Did you get word of a stormy exchange?
No, I do not remember that gentleman.
I did not hear anything, although I was there that day and was working in the nearby room. If there had been loud voices, a shouting match,
I would have heard something.
But it does not mean it did not take place, as my memory could be failing me.
There were indeed many high ranking visitors in Sture Linnér’s office, and I did not always necessarily get a look at them.
* Did Dag Hammarskjöld’s collaborators try to deter him from flying unescorted?
That is true, since I remember I heard about it.
They did try to deter him.
There were rumors that they were « waiting » for him in Katanga. There were Tshombe’s two Fougas.
(nota: in September 1961, the UN still believed two remaining Fouga were operational, as there was actually only one left, « 93 », the other one bing grounded awaiting spare parts)
When we heard about the crash, we immediately thought: « Tshombe’s Fougas did it ».
Personnally, I just could not imagine such a thing: who would want to shoot down the UN Secretary General?
I really thought this was just an accident, at least until after I left Congo early 1962.
If I had known … I was so scared in the air. I could never have boarded a plane.
But since I had no clue of what happened, I departed very easily when told to, without any further stress.
* Was Sture Linnér supposed to join the mission and fly along with Dag Hammarskjöld, as he later commented?
I was not at Ndjili airport but I would be surprised if he was intending to fly with them. It was logical for him to stay in Leo and liaise. That would be surprising if true.
Alice Lalande, she had to be part of the travelling party, since she was in charge of sensitive equipments, these Enigma machines. Besides, the Secretary-General needed an assistant like her. In her daily job, Alice was handing over paperwork to all the secretaries. She was a perfectly bilingual Canadian.
* Did Dag Hammarskjöld know that UN communications were intercepted?
I do not know, but it was a serious question for everyone in Leopoldville.
I had worked for weeks with Vladimir Fabry on the issue of the « frightfuls », these mercenaries.
I made dozens of photocopies from these documents that had been somehow collected and that had to do with these mercenaries. Vladimir Fabry worked a great deal on this issue. We did an extensive research on these documents. I am sorry that I did not have enough political awareness, to show an interest in the content of these documents.
* Monday 18 September 1961
Personnally, I did not get word of the crash when I arrived at the office on the next day. The other secretaries were doing a funny face, which was a bit intriguing. I made it late to the office due my long working hours on Sunday. I thought there was a dreadful atmosphere, but nobody told me anything. They did not dare tell me what had happened, probably because I was working so closely with M. Fabry. I only found out the same evening when I came home and my future husband told me: « did you hear what happened to Hammarskjöld ? »
* The crash site
When Mahmoud Khiary took off for Ndola, I came along.
(nota: on Tuesday 19 September 1961, in order to negotiate a ceasefire with Moïse Tshombé, as it was theoretically the case for Dag Hammarskjöld two days earlier)
I boarded the plane with him. If I had known the crash was foul play, I would never have come along with Khiary. This was so sudden, that I did not have the time to bring any equipment, not even a typing machine, as Alice Lalande had done.
We departed for Ndola. Prior to landing, while flying low over the forest, we managed to see the crash site from up close
(nota: the whole area was forested back then)
This memory will stay with me forever.
We spotted the wreckage, these scattered debris of an aircraft, what was left of it. This long line of burnt forest. It was terrible. I am still emotional about it, as I speak. I happened to realize the people I knew so well were only charred remains by now.
Alice Lalande, to begin with, who was basically my boss.
The security officers, such as Harold Julien.
I remember Alice’s dress with the flowery design. It sent cold shivers down my spine when I realized the plane had crashed and burnt that way. I though My God, she must have burnt so quickly. It was terrifying.
* Ndola, 19 September 1961
When we arrived in Ndola, there was this man, Lord Alport, welcoming us – so to say – at the airport. He was very cold. An extremely disagreeable character, very full of himself and every inch a British aristocrat. Still he invited our delegation for lunch in his home. I was just a secretary sitting at the end of the table with the security officers, but I found him disdainful towards us .
(nota : Khiary was not particularly welcome, since Tshombe had notified Linnér he agreed to negotiate a ceasefire with anyone but Khiary, whom he deemed responsible for launching Operation Morthor on 13 September 1961 – which is at least partially true)
Our mission was not very welcome.
Then we headed for the actual ceasefire negotiations with Moïse Tshombe, but I did not directly take part in the negotiations. The British mission there lent me a typing machine, whose keyboards had none of the French accents, which made my task very dfficult. I did however type all the ceasefire documents.
We stayed two or three days in Ndola.
Mahmoud Khiary and the delegation visited Harold Julien in the hospital. I was not allowed to join them.
1961 was a terrible year in my life. Annus horribilis, as the Queen Mother would say.
There was my being taken hostage, then Hammarskjöld’s crash, then the murder of 13 Italian air crew.
(nota: massacred by the crowd who mistook them with Belgian paratroopers in Kindu on 11 or 12 November 1961)
One of them was 25 and a very good friend of mine.
He had been at my wedding two weeks before, on 28 October 1961, along with Sture Linnér’s wife, whom I called Madame Linnér, of course, and also Jacques Poujoulat.
This day of September 1961, this Sunday the 17th. In my old age, I still cannot fathom what unfolded that day. It is still with me. It will stay with me until my last breath.

September 17, 2021, will be the 60th anniversary of the plane crash that killed our uncle Vlado, Dag Hammarskjold, and 14 of their brave colleagues while flying on a peace mission to Ndola, and we continue to wait for justice. For this reason, I am especially grateful to those who have no direct connection to the crash, who have made it their mission to help us uncover the truth with independent research and inquiry.
In July of this year, Joseph (Joe) Majerle III shared his own analysis of the crash with all the relatives, and it is an incredibly thoughtful and moving effort to support us. The points he makes deserve serious examination, and I want everyone to read it, so I am publishing it here in full – it offers a new perspective that was eye-opening for me, and lifted my spirits. Thank you, Joe!
AN ANALYSIS OF THE EVIDENCE CONTAINED IN RHODESIAN REPORT’S
ANNEXES II AND III AN D THE U.N. GENERAL ASSEMBLY REPORT A/5069 PERTAINING TO THE CRASH OF DOUGLAS DC-6B SE-BDY S/N 43559 ON SEPTEMBER 17-18, 1961
By Joseph Majerle III
PREFACE
I AM NOT a professional aircraft accident investigator. I am writing this account because
after reading the reports of the crash, the professional aircraft accident investigators
that were tasked with determining the facts of this tragedy, or for that matter, anyone
else that has viewed the evidence contained in the above–mentioned files, have not
come forward and pointed out the glaring misperceptions, dismissiveness of obvious
real evidence, and inappropriate focus on irrelevancies that shaped the conclusions of
the reports. In addition, there is at least one aspect that I can only describe as a
deliberate inaccuracy that I consider to be of decisive importance. The Annex III and U.N. A/5069 reports, following the original Board report, did not effectively question the
basic premises of the Investigating Board report as presumably would have been their
purpose; which is why nearly 60 years after the crash this subject is still very unresolved
for a surprising number of people.
I AM PRIMARILY, an aircraft mechanic. But, I earned a private pilot’s license and
had begun commercial and instrument flight training before earning any of my
mechanics ratings. Before I had any ratings at all, I had already built and flown my first
airplane out of salvaged, crashed, repaired and new parts. At this point, I was already
self-employed in the aircraft maintenance, salvage and rebuild business.
I started salvaging airplanes from crash sites in 1974, studying whatever evidence was
left at the scene in an effort to understand what and how the accident happened. With
the advent of the Internet and the posting of Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB) and National
Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) accident reports online, I have been able to read
many reports going back to at least to the mid 1930’s because I was interested in
learning what was known about particular incidents that I had heard about as a
youngster, and for well into adulthood.
I decided to abandon thoughts of becoming a professional pilot because at the
time there were probably ten newly qualified commercial and airline transport pilots
competing for every available job opening, and operators had their pick of the best. In
the maintenance field, however, it was the opposite story; at the flight school there was
only one mechanic, recently licensed, and not very confident at all in his abilities. As an
experienced, but not yet licensed mechanic, I assisted him in getting the flight school’s
grounded aircraft operational again. For all intent and purpose, I have never been
without work since.
I do not think it is inappropriate that I should be the person to write this report.
What is required here is a broad-based, general knowledge of aviation, aircraft, their
operations. I do not think an investigator has to have a DC-6 type rating to know how they are operated; provided one consults pilots with the rating to confirm what published documents like airplane flight manuals and Approved Type Certificate (A.T.C.)
specifications say. Here in Alaska, it is very possible that we currently have the largest
base of DC-6 experience operating, on a daily basis, in the world. I have known a great
many DC-6 type rated pilots in my lifetime, to say nothing of having been related to one
by marriage.
Any reader who wants to challenge what I state in this document is urged to
consult with their own “expert(s)”. I do not claim to be an expert on any aspect of this;
however every DC-6 expert that I consulted throughout this process confirmed readily
what I thought to be the case when I presented them with the evidence. So that is why I
think that it is time to reexamine what actually happened during the crash, as opposed
to what most of the world thinks happened. Because, the two are very different.
It is not within my area of expertise to speculate on the “why” of what caused the
precipitating action of this accident. I have read a number of reports and books over
recent years that attempt to tackle that subject, but I have nothing to contribute to what
other researchers, with apparent objective credibility, have amassed.
I am, however, bothered enough by the acceptance of the original Rhodesian
premises by the world at large and former U.N. officials, and the effect these
misconceptions have had on the descendants, relatives, and friends of the victims, crew
and passengers, that I am submitting this document to whom it may concern.
PREMISES
The Annex II report sets a number of premises that have gone unquestioned. They are,
and I will attempt to order them in terms of occurring chronology, as follows:
THE INSTRUMENT APPROACH
Annex II, part 3, par. 12.6 “. . .hit trees and the ground at a shallow angle of 5 degrees or
less, at what appears to have been normal approach speed, at an altitude of 4357 feet
MER (?) with its undercarriage locked down, flaps partially extended, and with all four engines developing power and all the propellers in the normal pitch range, heading
towards the Ndola radio beacon on a landing approach.”
There are four main parts of this statement to be addressed. They are to be
considered in light of the aircrafts position in relation to the Ndola airport, which
according to Annex II Part 1 par. 1 item 1.1 was “From Ndola aerodrome control tower
8.05 nautical miles on a true bearing 279 degrees.” 8.05 nautical miles is over 9.25
statute miles, from the airport at which it was intending to land.
01. “Normal approach speed” in my experience is based upon the aircraft’s stall
speed, landing speed, and minimum control speed in multi-engine aircraft. It varies with
combinations of all of the above and is normally calculated in percentages above the stall speed, which itself varies with differing weights, centers of gravity, bank angle,
flap/high-lift device deployment, etc. In standard airport traffic area there is also a
speed limit of 156 knots (180 mph.) Since the beginning of the age of the jumbo jets and
the airports from which they operate, the speed restrictions have been raised because
many of that class of aircraft have higher stall speeds than 156 knots (180 mph.), so for
them, there is only the 250 knots (288 mph.) below 10,000 feet rule, which I believe
applies to all airspace complying with ICAO rules.
Normal approach speed, at that stage of the approach, should have been 160
knots (184 mph.) or even more in this case, with this captain concerned about the
possibility of armed, hostile aircraft in the general area. In consultation with a DC-6
captain, he said except in very unusual circumstances the standard instrument approach speed up to the final approach fix, which in this case was the Ndola NDB, 2.5 nautical miles, 2.875 statute miles from the runway end, would be 160 knots (184 mph.)
Maximum flap extension speed is 139 knots (160 mph.)
The point that needs to be made here, and clearly with no ambiguity, is that there
would have been no reason whatsoever in a normal instrument approach, especially in
good weather conditions, to have had the aircraft slowed down to landing configuration
while over 9 miles away from the airport. Standard procedure would be to begin
deploying landing flaps and landing gear upon reaching the final approach fix, which in
this case was the Ndola NDB (non directional beacon), approx. 3 miles from the runway,
which is a fairly average distance for an NDB or a VOR (very high frequency omni-directional range) to be situated to a runway. That the aircraft was found configured for
landing at the farthest point it was going to reach away from the airport during its
instrument approach, means that the pilot would have had to slow-fly it throughout all
of the rest of the approach procedure to a landing at the airport. There is absolutely
nothing normal about that. This was the very first thing that struck me when I initially
read the report. It is indicative, however, OF A LANDING ATTEMPT AT THE LOCATION
WHERE IT CAME TO REST.
02. “. . .with its undercarriage locked down, flaps partially extended, . . .”
The DC-6 series aircraft have a stall speed of approximately 80 knots (92 mph.), and
consequently a lower approach speed than the jet airliners that replaced them beginning in the 1960’s. The closest replacement is the Boeing 737 series, which like the DC-6 have an approximately 30,000 lb. payload and were generally intended to operate from the same runways that the DC-series used. While the Boeing will neither take off or land and stop in as short a distance as a DC-6 due to its higher stall and approach speeds, the differences are not gigantic. For this project I consulted a Boeing 737 captain whose career spanned the 737-200 series thru the 900 series, and was told, again, that landing gear and landing flap settings were deployed upon reaching the final approach fix, which is generally approximately 3 miles from the end of the runway. This, in an aircraft with higher approach and landing speeds.
Wing flaps increase both lift and drag, and were originally developed to enable an
aircraft to make steeper approaches to land without increasing speed that would need to be bled off during rollout after touchdown, in other words to shorten the landing to a
stop distance. That they would also reduce the takeoff distance and improve the climb
performance was a secondary consideration. Annex II part 10 par. 10.3.4.2 states that all indications were that the flaps were in the 30 degree position. I would estimate that this is approximately optimal for lift and slow flight which would be desirable for the lowest approach and landing speed based upon experience with numerous different types of aircraft; I have flown a number of different airplanes with flap deployment angles beyond 35 degrees and noticed that at angles much beyond 35 resulted in much higher drag components than lift components and engineering books generally support that observation based on wind tunnel testing. The higher angles of extension were generally useful only for bleeding off excess altitude quickly in situations where a pilot wanted to get a lot closer to the ground in a hurry. To my experience, 30 degrees was optimal landing flap in many, but not all, types. Again, it is indicative OF A LANDING ATTEMPT AT THE LOCATION WHERE IT CAME TO REST.
03. “. . .with all 4 engines developing power . . .”
10.1.4 states “. . . the four engines were broken from their mountings and severely
damaged by impact and subsequent fire . . . .” Examination of photographs in the
appendix reveals that engines #1, 2, and 3 had fallen to the ground after the aluminum
nacelle structures melted away in the fire subsequent to coming to rest, and the straight steel tube struts of the actual engine mounts are still straight and attached to the engines. Furthermore, the above mentioned engines are all still in the approximate
positions they would have occupied on the wing with only the #4 engine having
detached in the crash sequence, and it is laying in probably very close proximity to
where it was wrenched from the wing during the cartwheel arc.
The second thing that struck me upon first viewing the wreckage plan is that almost
the entire aircraft is still in one place.10.2.1 “The main wreckage was contained in an
area approximately 60 feet by 90 feet . . . .”
The DC-6 is almost exactly 100 feet long with a 117’6” wingspan, which means after
it came to rest and cooled down the whole of the main wreckage would fit within the
same rectangle as its original size. The wreckage plan, as surveyed, indicates that the
vast majority of its original parts ended up oriented in the approximate positions that
they occupied prior to the crash. In other words, throughout the crash sequence, very
little of the aircraft was displaced from itself until very close to the end of its movement.
This indicates a low energy crash with a very slow speed impact, at least relative to even
minimum flying speed, to say nothing of a 160 knot instrument approach speed. 160
knots (184 statute mph.) is a velocity of almost exactly 270 feet per second. The wreckage plan length of 760 ft. from first point of treetop contact to ground strike of the fuselage nose (10.1.1) is approximately one half of what I have observed to occur in
unintentional controlled flight into terrain (CFIT) crashes during my time in this
business. It is, however, in addition to viewing the appendix photographs of the site that
were taken from the ground and from the air, completely consistent with the path of an
aircraft with an 80 knot stall speed being intentionally landed.
Aircraft that are only capable of even 120 knots in unintentional CFIT crashes
generally never resemble an airplane by the time all of the parts come to a stop, their
propellers are almost never still attached to the engines, their landing gear are almost
never anywhere near where they were originally attached, and their tail groups when
broken off have usually broken the control cables in overload displaying a “broomstraw” effect. In this case, when the tailcone broke off in the cartwheel there wasn’t enough energy left to pull the cables apart. If I had to estimate the minimum speed required to disintegrate the nose section of the fuselage such as is displayed in the wreckage plan and what can be seen of the remains in the photographs, I would say that it would require at most only about 50 to 60 knots to do that kind of damage. It was explained to me in 1986 by a good friend that was a DC-6 captain at that time, that the 4-engine DC-series had a somewhat fragile nose landing gear structure but not unusually so compared to other makes in it’s class; but when they tore out of the fuselage it often did a lot of other damage and could possibly make the incident beyond economic repair. I saw an example of that just last fall (2020) where a DC-4 had its nose landing gear torn out in a ditch at barely more than walking speed; the damage extended through both sides of the factory break joint where the nose (flight deck, cockpit) section attaches to the forward fuselage section and the operator decided that it was beyond economical repair, according to a conversation with his director of maintenance. This should reflect no discredit on the part of the designers; from personal experience repairing nose landing gear damage on many different types of nosewheel type airplanes it is generally a fragile part of all of them.
04. “. . .and all the propellers in the normal pitch range, . . .”
This statement stretches ambiguity beyond limits. The Hamilton Standard
43E60/6895A-8 propellers such as were installed on SE-BDY (of which I have owned
several sets and still possess a crate full of hub and dome parts) has a normal pitch
range of approximately 90 degrees from neutral for feathering and forward thrust and maybe 20 degrees aft of neutral for reverse thrust. 10.3.4.4 states: “Inspection of the propeller stop ring assemblies confirmed that the angular setting of all propellers was in the constant speed range.”
First, the stop rings do not determine the constant speed range; they are only the
outer limits of the blade travel, at full feather and full reverse. The constant speed range
is a function of the engine driven governor and the distributor valve assembly housed
within the hub and dome and is sensed with electrical switches attached to the blades
and actuated with an electric motor driven oil pump mounted on the engine reduction
gear nose case immediately behind the propeller hub, with a rubber/spring lip seal
interfacing the parting surfaces. The only way to determine the angular setting of the
blades in this installation is to measure with a propeller protractor against the rotational axis.
Second, the constant speed range is also a function of the engine turning at a high
enough RPM for the governor to supply enough boosted oil pressure to operate the
distributor valve to keep the blades off of the low pitch stop, which in reversing
propellers such as these is again a function of the distributor valve. But for the purposes of this analysis, that is not important.
Third, the photographic evidence, is what is important. The U.N. report appendix
contains photographs with 16-digit letter/number codes, of which I saved fifteen to a
file, beginning with S-0727-0004-01-00002, and following will be referencing the last
two digits. I will reference the individual blades in clock face numbers, as viewed from
the rear of the engine looking forward as is standard practice.
It is difficult to differentiate between engine#1 and engine#4 because there were
fewer views of #4, but both could be identified by orientation with the wreckage plan. It
is readily apparent that both of these had almost identical damage to their blades, except that the third blade on #4 is not visible. Photo 07 shows #4 with the 10 o’clock blade in standard reverse thrust position. The 2 o’clock blade has had its spring pack drives sheared in overload during the ground strike and has rotated on its pivot axis into an approximate reverse feather position, with its trailing edge forward instead of its leading edge when in standard feather mode. This indicates that its leading edge struck the ground hard enough to shear the spring packs while the leading edge of the blade was rotated aft of its plane of rotation, in other words while at a reverse thrust angle. With 2 of the 3 blades coming to rest in a reverse thrust angle, I think it’s safe to assume that the propeller was fully operating in the reverse thrust mode at time of impact.
The #1 engine is well represented in the photographs, with all blades visible.
Photo 16 shows the 10 o’clock blade in standard reverse thrust position, spring
packs intact. The 2 o’clock blade is in reverse feather position, spring packs sheared
as per the same blade on the #4 engine, and the 6 o’clock blade is also in standard
reverse thrust position, spring packs intact, but has bent aft throughout its length
progressively to the tip which is common when rotation is coming to a stop while the
engine and airframe behind it are still moving forward. That the propellers on
engines #1 and #4 are far less damaged than the ones on #2 and #3 is partially due
to the fact that they were mounted higher on the wings due to wing dihedral, and
didn’t penetrate the ground as deeply when they struck.
Photo 07 shows #2 engine with its 2 o’clock blade rotated into a reverse feather
position also, spring packs sheared. The broken off shank of what would be the 10
o’clock blade is in standard feather position, spring packs intact. What would be the 6
o’clock blade is not visible in this view, and I haven’t found any other photos showing it,
but based on its proximity to the ground I think it’s reasonable to assume that it also was sheared off during its ground strike.
Photo 33 shows #3 engine, which reveals its 2 o’clock blade broken off at what I
would estimate at most to be its 25” station, which is measured from the propeller shaft
centerline. It is clearly in a standard reverse thrust position, spring packs intact. The 10
o’clock blade is broken off 1.5” to 2” outboard of the hub clamp halves, so close to its
round shank section that its angular position is inconclusive. The 6 o’clock blade has
broken off inside of the hub clamp halves through the blade bushing bore; it obviously
fragmented into a number of pieces. As with all three of the other engine’s propellers, I
think it is reasonable to assume that the #3 propeller was fully in the reverse thrust mode when the blades struck the ground. I would deduce from the condition of the #3
propeller that it was positioned to penetrate the ground the deepest and most solidly of
the four. The #3 engine also received by far the most fire damage after coming to rest
most likely due to its proximity to the most remaining fuel in the right hand wing. I will
discuss this in more detail later.
I have thought long and hard about how to estimate how much power the engines
were developing at the moment the propellers struck the ground, and it is a difficult
question. The propeller blades were group 4, an early post-war development and were
the strongest of all the Hamiltons ever built for piston engines, generally used only on
the latest and most powerful post-war radial engines. I am not aware of any empirical
strike strength tests, which is not to say that Hamilton Standard didn’t conduct any, I
just haven’t heard about them. If I had to guess I would estimate that it would require a
high-cruise manifold pressure setting to shear them off and break them through the
blade bore bushing hole as is evident in the photos. The captain clearly had gotten the
throttles well forward and was making a lot of reverse thrust before the nose landing
gear collapsed and the nose and propellers hit the ground.
THE WRECKAGE PLAN
The Annex II wreckage plan and the photographs of the descent path appear to show a
deliberate, controlled descent with directional control maintained all the way to the
anthill, as though it was intentional, and I am suggesting that it was.
I had difficulty scaling the exact measurements of where the small parts that
were torn from the aircraft came to rest relative to the initial tree contact, and varying
figures are given for the height of the anthill from 9 to 12 feet, which I would have
thought would be consistent with the whole site having been charted by professional
surveyors, but in reality this is not important.
What is important is to realize that only 760 feet from initial treetop contact the
aircraft was rolling with all three landing gear on the ground, right side up, travelling in
a straight line, directionally under control.
At some point not far from the anthill the left wing bottom skins were breached,
presumably by a tree trunk, the top of which would have been broken off by the wing
leading edge and spar(s), opening up one or more fuel bays and dumping their contacts
to the ground in a concentrated area, which fueled the incinerated area shown at that
location in the wreckage plan. As stated earlier, this would contribute to the reason that
the #1 and #2 engines on the left side of the aircraft were less heavily fire damaged post-crash than the engines on the right side. However, the overall strength of the main wing box structure remained sufficiently adequate to retain its basic shape to provide the arm about which the entire aircraft would pivot upon striking close to the base of the anthill, leading edge down, and not be sheared off at that point. Obviously, the wing leading edge outboard of the engines is what actually contacted the anthill, and initiated the cartwheel, as both of the left hand engines stayed with the wing and came to rest close to their original positions on the wing.
At some point close to the anthill, (and somebody could probably do a better job
of quantifying the actual measurement from the wreckage plan), but it is not marked as such, the nose landing gear structure was overloaded in the undisturbed forest terrain
and collapsed. Which is to say that the oleo strut and its retraction/extension linkage
was torn from its mounting structure and its broken pieces were spread along the
ground from forward movement of the rest of the aircraft behind it. I looked long and
hard in the wreckage plan to find the exact point where the nose gear departed, but
could only find reference to a “steel shaft” alongside the base of the anthill, and couldn’t
find it in the photos. Presumably, the “steel shaft” was the nose strut piston tube, which
is a steel tube approximately 5” in diameter, and it was about where I would have
expected it to be in this case. Other associated parts of the nose gear system were a little farther along the path, again where I would have expected them to be. I could find no reference to where the nosewheel and tire came to rest, which is important from the
standpoint of knowing how long it was on the ground before failing, which was in some
measure the fate sealer for the crew and passengers. I did find reference to an
unidentified portion of wheel rim on the right hand side of the path and well before the
anthill, but whether it was from the nosewheel or one of the dual main wheels may
never be known. Photo 19 shows one of the main landing gear assemblies with the
remains of both tires and wheels in place and another photo shows the same for the
other MLG, so it is certain that all of the main wheel tires stayed in place throughout.
While on the subject of the main landing gear, the DC-6 MLG units retract forward into
their nacelle bays, and their retraction/extension links for normal operation on the
ground loads the links in tension, which for metallic structures allows them to be at their strongest, especially in terms of retaining their shape when loaded. The photos show that the links had failed in compression and had bent, which would be expected to happen upon the main wheels striking the ground while traveling backwards during the cartwheel, and partially retracting back into their nacelle bays. But, effectively, they
stayed in place throughout the crash, again indicative of a relatively low speed
occurrence.
As stated above, shortly after landing with all three landing gear on the ground,
close to the anthill, at probably the worst possible location and time, with all four
engines evenly at fairly high power settings in reverse thrust in what would have been a
desperate attempt to slow the momentum of the aircraft and get it stopped, (but what is in reality standard operating procedure), the nose landing gear collapsed, instantly
dropping the nose section of the belly and fuselage to the ground, pivoting on the main
wheel axles. When this happened, the propeller blades began contacting the ground,
bending and breaking them off, and the wing leading edge from end to end rotated
downwards, drastically lowering in height. As the fuselage nose belly skins, stringers,
formers etc. began crushing and tearing away it allowed the wing leading edge to get
even closer to the ground, until the left side contacted the anthill nearer the base than
the top, which initiated the cartwheel. Had the nose gear remain in place, there is at
least a chance that a relatively level wing might have been able to ride up and over it and the aircraft’s momentum to remain linear, and with even a few more seconds of reverse thrust as braking action, the survival odds would have increased dramatically.. The noted fragment of wheel rim found along the glide path, if from the single nosewheel, and if large enough to have allowed the tire to depart from the wheel, I think in this terrain would have guaranteed the failure of the nose gear assembly.
I think a further word here about center of gravity is appropriate. SE-BDY as it
departed Leopoldville was handicapped with a forward C.G. (center of gravity), with
little or no aft cabin load. The DC-6, as with all large airliners, was designed to carry its
nominal 15-ton payload distributed throughout the cabin from end to end and as with
most aircraft have the load approximately centered on the wing, since that is what is
supporting everything. In this case, with the passengers and their gear in the forward
part of the cabin, the C.G. would have been well toward its forward limit, known as nose
heavy. This means that the pilot, under any circumstance, would have a harder time
holding the nose off the ground with the elevators than if there was weight in the
fuselage behind the main wheels assisting him with the balance.
I have flown airplanes with only the pilots in the front seats and nothing in the aft
cabin where the nosewheel could not be held off the runway whatsoever upon landing.
With power at idle, when the main wheels touched the nosewheel slammed to the
runway instantly because the C.G. was well forward of the mains. At least three different DC-6 pilots I have known over the years have told me that they much preferred flying them with a somewhat aft C.G. because of the better balance. In this case however, I think it could be listed as a contributing factor to the deadliness because after getting the main wheels to the ground, with the propellers in reverse and no accelerated air flow over the elevators, the captain was unlikely to have been able to keep the nosewheel from slamming to the ground immediately and beginning the sequence of breakup of the forward fuselage structure.
ABOUT THOSE ALTIMETERS . . .
There are numerous references throughout the reports about the barometric altimeters, three each, forming one of the major premises upon which the reports conclusions are based. So many, in fact, that I am not going to bother referencing them here. The Board (Annex II) and the Commission (Annex III) both spared no expense to prove beyond any shadow of doubt that the their Air Traffic Control (ATC) had properly informed the crew of the altimeter setting and that Transair had properly maintained their instruments and aircraft, as well, and that there should be no discredit reflected upon the servants of and the country hosting the visitors. If those visiting aircrews could not pay attention to their altimeters and keep from flying into the ground while executing an otherwise exemplary instrument approach it was not the host’s fault..
There is one very major problem with this.
There were four altimeters installed in this aircraft. The fourth altimeter was an
“AVQ-10 Receiver Transmitter (Radar) “, per Annex II Par. 6.2 Page 15, line 3. That, and a
reference on the “Enlarged Portion of Wreckage Plan” to a “Radio Altimeter” on the
extreme left hand side of the page are the only times throughout all of the original
reports that its existence was ever mentioned.
And it was decisively important.
Mankind had long awaited a means to know exactly how far the ground was
below you and how far away an obstacle was in front of you while making instrument
approaches. Barometric pressure gauge instruments were reliable but didn’t give you all the information you really wanted and needed for making truly blind instrument approaches. With the WWII British development of the cavity magnetron, which made
radar small enough to be carried aboard aircraft, it was a short step away to build an
accurate radar altimeter. The DC-6 was among the very first of the postwar civil aircraft
to be fitted with them. By then, airlines couldn’t afford not to have them. And all of the
pilots that I have ever known use them when they have them during instrument
approaches especially when near the ground. They tell me that they are a very
reassuring and confidence-building device.
It is inconceivable that captain Hallonquist was not using the radar altimeter, if
he needed an altimeter at all, throughout the portion of the instrument approach that
the aircraft completed. Barometric altimeters are fine for flight where there are large
safe heights above ground level and sufficiently accurate for keeping airplanes at known levels relative to each other but when you start getting close to the ground in conditions of poor or no visibility the radar altimeter is what is going to tell you where the ground or a solid object is in front of you.
I mentioned above about needing an altimeter at all. In the USA, in order to
qualify for a private pilot certificate, a student must accomplish a certain number of
landings and fly a certain number of hours at night during official after-sunset periods,
(night time). This must be accomplished visually, under official VFR (visual flight rules)
conditions. I am fairly certain that the rules to qualify for airman certificates in Sweden
or the UK would be pretty similar, and in fact for all ICAO (International Civil Aviation
Organization) countries. Without access to his logbooks, it’s a foregone conclusion to
assume that with over 7800 flight hours captain Hallonquist was competent and
comfortable with night VFR landings. On the night in question, the weather 38 minutes
before the crash, per Annex II chap. 5 par.5.3 page 14, the visibility was 5 to 10 miles
with slight smoke haze, with ceiling not given, but presumably nil cloud cover from the
last prior routine weather observation, 3-1/2 hours before. So there is no reason to
assume that the crew couldn’t see where the ground was.
Prior to the advent of aircraft with auto-land capability, which was probably not
until at least the mid-1970’s and to my knowledge didn’t come into service until the
early 1980’s, all, at least all civilian airplane landings were made visually by the human
pilot. Even instrument landings were made visually, even when the approaches were
made coupled to an autopilot. If at some minimum height above the ground at some
certain distance from the end of the runway, and these numbers varied with different
airports and with differently equipped aircraft, the pilot could not see the end of the
runway to land the approach was called missed, power was applied and the aircraft
climbed away to either try the approach again or proceed to an alternate airport where
the weather was hopefully better. But all landings required the pilot, at some point, to
see the runway visually. And the pilot was only using the altimeter to know where to not
descend below. To this day, the vast majority of airplane landings worldwide are still
done this way.
Upon reaching Ndola, the aircraft established communications with the tower
informing them that they had the airport in sight. At that point the captain could have
made a VFR landing within the airport traffic area (ATA) without following the
instrument approach procedure. Transair company policy was that if the crew was
unfamiliar with an airport, and captain Hallonquist had never been to Ndola before, an
instrument approach was to be made. The captain could have ignored this but he was obviously the type of person that would rather follow the rules and go by the book than
ever have to explain in the future why he did not. I fully understand this philosophy, it is
how I’ve tried to live my own life. It can be well imagined that for an instant it crossed
his mind that he could just set up and land while he was right there, but he knew that an instrument approach was just a few minutes more, no big deal, we can see the ground, no appreciable weather. In other words, he didn’t really need an altimeter to tell him where the ground was. He could see the ground. And the radar altimeter told him exactly how high above the ground he was.
THE PRECIPITATING EVENT
To my observation, in the study of aircraft accidents throughout the course of my life,
there is almost always a precipitating event that sets off a chain of actions, reactions,
counteractions, etc. that results in the crashed aircraft somewhere on the surface of
earth. In this case, it is known from Annex II that the captain communicated to Ndola
tower that all was well and within minutes the aircraft was being incinerated with its
own wing fuel and that fifteen of the sixteen occupants lives had ended, and that the last would succumb in less than a week. That person, Sgt. Harold Julien, was the only
eyewitness to the crash.
To my experience, eyewitness testimony is considered evidence in a court of law,
at least in this country. I am unfamiliar with Rhodesian law in the 1960’s, but in the USA
in the 1960’s Sgt. Julien’s statements would have been considered evidence in a crash
investigation. Since there is no other actual evidence to the contrary, and testimony of
ground observers about the airport over-flight and entry to the instrument approach
procedure are insufficiently conclusive to determine externally what the precipitating
event was, it seems logical to me that Sgt. Julien’s statements, as brief as they are, are the only thing that can be considered as evidence in a search for the cause of the chain of events leading to the crash.
In the UN Commission report, par. 129., Senior Inspector Allen testified to the
U.N. Commission that he spoke with Sgt. Julien and asked him three questions; 1. “What
happened? He said: ‘It blew up’.” 2. “Was this over the runway? And he said ‘Yes’. “ 3.
“What happened then? And he replied: ‘There was great speed—great speed’.”
“It blew up—”
“—over the runway.”
I have read all three of these reports several times and still don’t understand the
reluctance of the investigators, including the U.N. and the Swedish observers, to not
make those six words the central point, the number one item on the list of where to
begin to find the truth about what happened. Especially from the standpoint of
determining whether or not there is fault to be assigned to the flight crew.
Assuming Sgt. Julien was belted into any seat in the forward cabin, looking out
the side window on whichever side he was sitting on, he may or may not have had a
view of the lighted runway and the town of Ndola but it is likely that the captain would
have informed the passengers that they had arrived overhead Ndola and would be
setting up to land there. It would have been the last thing he could identify location-wise and anywhere in that vicinity for him would be “over the runway”. I don’t know if Inspector Allen was deliberately trying to trip him up or why he asked him if it was over
the runway when he knew that the aircraft had overflown the runway and not blown up
there, but, it seems to me, it was an unusual question to ask a person in Sgt. Julien’s
condition. What I am getting at here is that Sgt. Julien knew where the runway was and
that the aircraft had blown up. They sound like lucid answers to me, and not as though
he was thinking about horses or submarines, for example.
In my view, in light of all of the data and evidence of all of the pages of all of the
reports and the information displayed in all of the images of all of the photographs in the U.N. file, the only thing I can see that qualifies as a precipitating event is Sgt. Julien’s: “It blew up”.
And he was the only one left that was there when it happened.
Airplanes have been blowing up for a long time, in fact for almost as long as
they’ve been in existence. There is a lot of video of it happening; I can think of footage
that I’ve seen going back to the 1920’s. And I’ve been on-scene to ones within seconds to minutes after the explosion. I’ve salvaged wrecks after the fact, and studied the effects of explosions on structures and materials.
To my experience and observation, on metallic structures, if some event ignites
the fuel vapors, it is the vapors that explode and the still-liquid fuel then burns, but the
explosive event is by then over. During the explosion some weak area in or near a seam
will give way and tear open, leaving, in effect, a chimney from which the burning fuel
would exhaust. In aluminum stressed-skin wet wing or bladder tank explosions, there is
usually a torn section of skin along a rib or a stringer or even a spar, (weakened because of the drilled holes for rivets) that has opened up and from which the the fire burned upward out. I have never seen an example where the fire burned downward; only upward. Presumably, because heat rises.
In viewing video of air combat, of which many hours exist of footage of most of
the combatant countries back to at least WWII, when an airplane being shot at catches
fire and smoke begins trailing behind, it is subtle but noticeable that the flames are still
burning upward and the smoke is trailing slightly upward.
Another thing that struck me when I was standing near a burning airplane at
night, while the fire department was trying to extinguish it with water, which was rather
ineffective, was how brightly a gasoline fire lit up the sky in the dark.
As stated earlier, aircraft fuel tanks have been blowing up resulting in the
destruction of the aircraft for a long time, for a number of reasons. The incendiary
(tracer) bullet was developed during WWI to ignite the hydrogen gas in enemy airships
and observation balloons, and was very effective, not only for that purpose but also to
ignite the fuel in airplane fuel tanks. As TWA 800 proved in 1996, chafing electrical
wiring after arcing long enough could blow a hole through an aluminum alloy sheet and
ignite fuel vapors that would explode the tank so violently that it initiated an inflight
breakup. About two weeks after that, right here in Alaska an engine failure on a DC-6 led to a chain of events that resulted in ignition of one of the wing fuel tanks which was left to burn long enough to result in the wing folding up and an inflight breakup.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD)(static electricity) igniting empty or only partially full fuel
tanks was known to have damaged or destroyed (I am going by memory here) about 25 civilian turbojet airliners and comparable heavy military aircraft (bombers, tankers,
transports) combined since the introduction of the jet age. For that reason, after an
airliner lands at an airport and taxis to its gate and shuts down, along with chocking the
wheels a ground cable is attached to a fitting in the structure to remove the static charge it has built up while flying through the air. An airline line mechanic colleague tells me that he has measured as much as 50 volts upon making that connection.
But ESD is unlikely to have been the cause of the explosion that SE-BDY
experienced. However, the explosion that Sgt. Julien described is most likely to have
been the precipitating event that caused captain Hallonquist to make the decision to get the airplane on the ground, now, immediately if not sooner.
FORCED LANDINGS
Forced landings have happened throughout history for nearly countless reasons, but
several of the reasons account for the vast majority of the occurrences. Topping the list
would be engine failure; if your engine fails you have no choice but to put it down
wherever you happen to be. That would be in the involuntary forced landing category. In the voluntary forced landing category, and some statistical database could prove me
wrong, but to my experience inflight fire would be at the top. I have before me a list of
seven airplanes that I had some thread of connection to in some form or other that were force landed by their pilots into whatever terrain was below them at that moment
because it was the only chance they had to stay alive. One of the seven, the
aforementioned DC-6, technically doesn’t qualify as an attempted forced landing,
because of the captain’s indecision, but all of them resulted in aircraft that never flew
again, and in five of the seven all survived, but with some minor injuries. In the other
two, there were no survivors. The incidents I am referring to here all occurred in Alaska
since 1977, and it is likely that there have been others that never came to my attention.
All seven of them were due to inflight fires. One of the seven was a new customer of
mine, but the aircraft was one I had never and was destined to never work on.
After almost five months of examining these three reports, the conclusion I would draw
is that the case of SE-BDY fits into the category of a voluntary attempted forced landing
due to an inflight explosion and fire that was successful until its final seconds, and then
an unseen and un-seeable solid object ended its chance for a successful termination.
THE LAST ACTIONS
I will attempt to re-create the final minutes of the flight of SE-BDY based on the
information in the reports, as I would visualize it to have to have occurred. I want to
remind the reader that the largest airplane that I have ever steered through the sky was
a DC-3, which is for all practical purposes not all that different from a DC-6. The ancillary
control systems in the DC-6 were substantially different in being mostly electrical relay
controlled, it had two more engines, and there were more systems in general such as
anti-detonant injection (water/methanol) for the engines, reversing propellers, BMEP gauges for fine-tuning engine power and fuel mixture, etc.; it is a considerably more
complex machine. But for the purposes of understanding what actions were taken and
their results, it would have been basically as follows:
01. The aircraft has descended from the east toward Ndola from its reported
maximum cruise altitude of 16,000 ft. and establishes communications with the
control tower. It has just flown a long trip, far out of its way to avoid aircraft
hostile to U.N. personnel and has avoided radio transmissions as much as
possible to avoid detection. The captain states his intentions to enter the NDB
instrument approach and is told to report reaching 6000 ft. There are no further
communications with the tower.
02. It is likely that at last communication with the tower that the aircraft was already
at 6000 ft., based on airport personnel statements and the extreme likelihood
that the captain already had the Ndola approach plate in front of him, and had
based his descent rate into Ndola to arrive near the minimum descent altitude
(MDA) for the area.
03. The aircraft turns onto the outbound course leg and airspeed adjusted to at least
160 knots indicated airspeed. The Ndola approach plate in the U.N. report
appendix gave times for approaches at 180 and 200 knots in addition; there is no
way to ever know what speed was actually used. My best guess is that it would
have been 160 knots.
04. At some point approximately but probably more than half way on the outbound
leg course the precipitating event occurs. There is a bang, a flash of light, and
then a constant partial illumination of the night sky on the left side of the
aircraft.
05. The captain looks out the left cabin window and sees a section of the upper wing
skin torn open upwards, with bright yellow flames billowing rearward behind
that area. It is possible that he can feel some diminished lift component from the
spoiler-effect of the damaged wing skin on that side, and may have moved the
aileron trim to compensate.
06. Seeing this, the captain realizes quickly that they cannot expect the wing to last
long enough for them to make it the three or more minutes it would take to get
back to the Ndola runway; that they probably have only some number of seconds
to live. He determines that he is going to land the airplane onto the ground in
front of him, whatever that looks like, before the airplane breaks up. He is not
going to waste the time it takes to inform Ndola tower of the situation; flight
crews generally never do. Investigators wish they would.
07. With his right hand he reaches up and pulls the throttles back; with his left he
holds some back pressure on the elevators and with his right hand then starts
trimming the elevators nose up. Airspeed begins to decrease, heading toward
flap extension speed.
08. The captain has already told the first officer and flight engineer his intentions;
they are assisting him in the other physical actions necessary to configure the
aircraft for slow flight and landing. It’s possible that the first officer is also
assisting him in holding pressure on the ailerons to keep the wings level.
09. The aircraft is slowing down into flap extension range, beginning to descend, the
captain is trimming the nose up on and off, waiting to get down to landing gear
extension speed, for a large drag component to bleed off the excess altitude. The
captain is nominally staying on the turn-back arc of the instrument approach.
10. The aircraft has slowed enough for landing flap angle, then landing gear speed is
reached and the captain calls for gear down.
11. With the aircraft slowed well down, in an effort to speed the descent and get rid
of the excess altitude, the captain pushes the nose down with the elevators. The
wind noise increases, and with the nose down attitude the occupants get a sense
of “great speed”, but in reality the DC-6’s landing profile is comparatively steeply
nose down in normal conditions, opposite that of jet airliners, that land steeply
nose up. The large double-slotted wing flaps, and modest wing loading allow for
impressively steep descents at comparatively low airspeeds.
12. Seeing and sensing the proximity to the treetops, the captain begins putting back
pressure on the control column, judging the round-out with the experience of
1445 hours in DC-6’s, and rolls out of the procedure turn onto the return course
to the NDB. He is possibly helped in his depth perception sight picture by some
of the small campfires that the local charcoal makers have burning sprinkled
around the general area. He probably doesn’t need landing lights; they are useful
for illuminating reflective objects and lighter colored areas/objects, but can be
only distracting if there is nothing light to reflect.
13. Having leveled off just above the treetops, the captain retards the throttles to
idle and holds back pressure on the elevators and adds more nose up trim to
relieve the pressure, bleeding off more speed toward the stall. It is possible that
the thought occurs to him for a few thousandths of a second that if he makes it
through this, in the future he will insist on having some ballast in the tail on
these otherwise fairly empty charter trips. Now would be a good time to be a bit
tail-heavy.
14. The aircraft is gently settling, the treetops are beginning to brush the belly, the
propellers are chopping off twigs, there are probably some unfamiliar sounds
resulting from this.
15. The ever-increasingly sized tree branches are clattering off the sides of the
fuselage from the propellers now, the sounds of tree trunks snapping off beneath
the belly and wings can be heard clearly. A somewhat larger tree trunk contacts
the left wing leading edge a little inboard of the tip rib and shears through the
light skin, stringers, etc. and the wing tip falls away to the ground. That left wing
just can’t be held up quite level, but the aircraft is still traveling straight, into a
little darker darkness.
16. The captain throws the propeller switches into the reverse thrust position as a
group with his right hand and when the propellers start translating he reaches
for the throttles and begins advancing them forward.
17. The aircraft is halfway or more to the ground and the trees are breaking off
lower and lower. The manifold pressures are coming well up and the engines are
roaring, the propellers are chopping off ever-increasing sizes of limbs and
trunks. The reverse thrust in addition to the arresting effect of the bending and
breaking trees are having an effect; the aircraft is well below stall speed now. Landing gear doors are being battered and tearing off, as well as pieces of wing
skin, wing flap skin, and possibly horizontal stabilizer leading edge skin.
18. The aircraft has made it to the ground; all three landing gear are on the forest
floor. The burning left wing has not had enough time to shed molten sections of
skin yet, due to the occurrence at pattern height and the captain’s immediate
decision to get the airplane on the ground.
19. The left wing pushes over a larger tree, probably just outboard of the main
wheels that doesn’t surrender easily and tears a sizeable hole through the
bottom wing skins, instantly dumping a significant quantity of already burning
fuel onto the ground.
20. Some or all of the flight deck crew could possibly, for some very small fraction of
a second, think that this might turn out OK. They are on the ground, upright, still
largely in one piece, all still strapped into their seats, uninjured.
21. The aircraft at this time is effectively a 38-ton bulldozer, mowing down trees on
a forest floor that has probably been undisturbed for centuries, if not millennia; I
don’t know the history of that area. Except that it’s not built like a bulldozer, and
I doubt that one has ever been built that would move at whatever speed it was
going at this moment on its own. The nose landing gear at this time cannot
withstand the combination of ground roughness, imposed weight, speed,
possibly flat or even missing tire, and/or other unknown factors, and collapses,
tearing out and further weakening the surrounding structure. The forward
fuselage and nose section have pushed the nose gear down to its collapse, and
relieved of its resistance continue to plunge downward, crushing and tearing the
light aluminum structure to pieces as the forward shifting center of gravity
exacerbates the situation even further, as it is effectively standing what
originally was a 100 ft. long fuselage on its end.
22. Immediately after this, with the nose section disintegrating, the wing leading
edges rotated downward, and well powered-up engines and propellers slicing
the ground, the left wing leading edge contacts near the base of the anthill, and
the 38 ton mass with still considerable momentum rotates around it, side-loading the second fuselage section that attaches presumably to the front spar
section of the wing, ultimately severing it.
I don’t think I need to go any farther with this; I assume the reader knows the rest of the
story.
For the aircraft to have been found as described and photographed in the reports, it
would have had to happen generally as I have described. A type-rated DC-6 captain
could certainly provide more and better detail of the specifics of operations and actions,
and a mechanic with a lot of DC-6 experience could provide more and better detail of
how things worked in this case, and here in Alaska there is and has been a lot of DC-6
experience, but to my knowledge none have researched this case and come forward with their observations. I suspect that most who are currently alive are unaware of it. I don’t think I had heard of it until maybe ten years ago at the most. But, those who were aware of it at the time, even as children, have kept the account of the crash alive, and rightfully so, as it is an injustice to the memory of those whose lives were cut short.
In my view, the flight crew did everything right. I can’t see a single place where I
wouldn’t have done the same thing in that situation. I can’t imagine that approach
through the trees and the touchdown on the forest floor to have been accomplished
more skillfully by anyone I’ve ever heard of, Eric Brown or Bob Hoover, anybody. I can
only hope that I would instantly swallow my fear and act decisively in a similar situation,
as this captain and crew did. They are as shining an example to all that it can be done, as others I have known and have heard of have done, as there is.
To me, it is really, and I mean really, obvious what happened there.
I have written this for the offspring, the relatives, and friends of the victims, in hopes
that the dark cloud of implication that has surrounded this crew, completely
unreasonably I believe, for some six decades now, can finally be lifted.
Joseph (Joe) Majerle III
Anchorage, Alaska
July 2021
With gratitude, “The Elusive Truth About the Death of Dag Hammarskjold”, written for PassBlue by the son of Heinrich A. Wieschhoff. I’m sharing it here in full so everyone will read this, and know how the relatives truly feel about the UN investigation.
“My clock radio clicked on. The morning news bulletin announced that United Nations Secretary-General Dag Hammarskjöld’s plane was missing.
It was Sept. 18, 1961. I was 16.
Over the next hours, my mother and sisters and I learned that Mr. Hammarskjöld, accompanied by Dad and 14 others, had flown from Leopoldville, in the Congo, to Northern Rhodesia (now Zambia); that the plane, a DC-6, had not landed at Ndola, its destination; that an unexplained 15 hours went by after the airliner passed over the Ndola airport and before its wreckage was found lying not far from the runway; that all on board save one were dead.
My father, Heinrich A. Wieschhoff, was one of Mr. Hammarskjöld’s political advisers. Their party was headed for talks with the head of the breakaway Congo province of Katanga in hopes of quieting the fighting that had broken out between UN peacekeeping troops and the largely mercenary-led forces backing Katanga’s secession. It was a dramatic moment in the history of this mineral-rich country — a year after it gained independence from Belgium and quickly became embroiled in a violent quagmire involving the interests of not only Belgium but also France, South Africa, the Soviet Union, Britain and the United States.
Days after the crash, we learned that the sole survivor had died. Now there was no one to shed light on what had occurred. My family’s experience was lived in one wrenching way or another by the families of the 15 other victims. The particulars were different; the pain was the same — and only worsened because no one could tell us why the plane had gone down.
From the outset, there were legitimate concerns about the possibility of foul play. Within months of the crash, three inquests were held in rapid succession. The report of a UN commission, relying to a large degree on groundwork done by the-then Rhodesian Federation, was inconclusive, as was a report by the federal civil aviation body. The report of a commission empaneled by the Federation arrived, by a curious turn of logic, at the convenient conclusion that the event was an accident.
At first we assumed the UN would be vigilant in looking for new clues and dogged in running them to ground, and for years that seemed to be the case. Dad’s UN associates fielded our questions about the results of the original investigations and new allegations of wrongdoing promptly and graciously.
Once those associates left the UN, however, I gradually began having doubts that anyone in a leadership position cared much, if at all. One exception was Jan Eliasson, the deputy secretary-general under Ban Ki-moon, who was seemingly alone in advocating a serious look at the death of his idol and fellow Swede, Mr. Hammarskjöld.
The UN’s public posture toward Mr. Hammarskjöld drips with veneration — naturally. Yet when it comes to actually unraveling the circumstances of his death, a certain callousness prevails, despite high-sounding pronouncements to the contrary. In my experience, concern about the other 15 victims is even lower.
One byproduct of this indifference has been a coming together of nearly all the families of the deceased. Partly as a result, I have sensed that the UN is paying more attention to their interests, at least in its public comments. Privately, I still encounter telltale signs that the organization views the search for answers as a housekeeping matter.
For instance, when a group of the relatives sent the UN Secretariat a copy of a letter thanking the UN members sponsoring a recent resolution bearing on the crash, the response was a form letter from the public inquiries team stating that “the matter you raise is one of domestic jurisdiction, and does not fall within the competence of the United Nations.”
In 2011, the inquiry hit a turning point. Susan Williams, who had no prior connection to the crash, published “Who Killed Hammarskjöld? The UN, the Cold War and White Supremacy in Africa.” A sobering probe of information that the three post-crash inquests did not have, or had but failed to consider properly, it presented the UN with a chance to dig deep.
Dr. Williams, a historian and senior research fellow at the University of London, did not identify a likely cause of the disaster, but she did present a number of startling claims, including that US intelligence services allegedly eavesdropped as an unidentified plane attacked Mr. Hammarskjöld’s during its landing approach.
The book sparked hope that the UN would finally give the crash its due. First, however, a group of private citizens established a pro bono commission of four jurists to evaluate her findings. In 2013, they determined that significant new evidence could justify reopening the UN’s original investigation.
The stage was set, at long last, to bring this unhappy affair to a definitive close. Unfortunately, instead of insisting that further exploration be unlinked from the agendas of individual member states, and Secretary-General Ban be given a free hand to deal with the crash as he saw fit, the office of the secretary-general solicited the views of certain members of the Security Council. Predictably, influential members signaled their lack of enthusiasm for a full-fledged re-opening of the investigation.
In other words, the UN ducked — in my view, avoiding discomfiting questions about the roles of Belgium, France, South Africa, the Soviet Union, Britain and the US in events related to the crash, and possibly about the UN’s own handling of its original investigation and subsequent new evidence as well.
What followed was five years (and counting) of a piecemeal, woefully ineffective process fashioned to give the impression of rigor. Through resolutions organized by Sweden, the General Assembly first relegated the crash to a “panel of experts” for yet another assessment of new information (2014), then to an “eminent person,” the former chief justice of Tanzania, Mohamed Chande Othman, for follow-up (2016).
The resolutions asked member states to search their archives for relevant material and to declassify sensitive records, namely intelligence and military files. But genuine cooperation from the key players has been slow and halting. Russia and the US, as of a recent date, failed to comply fully with the General Assembly’s resolutions, and South Africa and Britain appeared bent on frustrating the process altogether. To my knowledge, the UN has rarely generated information on its own, so that leaves Chief Justice Othman to rely heavily on private sources.
As far as I am aware, the Secretariat has not engaged at a high level with recalcitrant member states to get them to adhere to the General Assembly resolutions. It has done little to publicize the activities of the chief justice. It has been slow to fully declassify its own archives and still refuses to release some documents.
In their Dag Hammarskjöld Lectures, in Uppsala, Sweden (Mr. Hammarskjöld’s home base), Secretaries-General Ban and António Guterres each mentioned the search for the truth about the crash but at the tail end of their presentations, almost as an afterthought. Instead of taking a meaningful stand, they repeated the hollow refrain: the UN was doing all it could do to find answers and member states should comply with the call to declassify relevant records.
Equally revealingly is the fact that in 2017, Secretary-General Guterres’s office sought to end the Judge Othman probe. Thanks to Sweden’s insistence, the General Assembly renewed his appointment. Did the secretary-general tip his hand last year when, rather than appear in person before the General Assembly, he sent a subordinate to present Judge Othman’s interim report?
His findings were impressive, especially considering his meager support. For his current engagement of about 15 months, Judge Othman has only himself and an assistant, working part time and in different countries, on a budget so small that nearly a third will go toward translating his reports into the UN’s official languages.
The opportunity presented by Dr. Williams and the jurists’ commission still stands. And we may learn more from Judge Othman’s final report, due this summer. I worry, though, that unless that report or a new sense of purpose by the UN can pry the facts out of Britain, the US and other key states, what happened and why will once again fade unanswered into the past.”
In memory of the 16 who died in Ndola, here is some of the collection from my mother-in-law, Olga Fabry, who carefully saved all the documents and mementos I share here. Vlado was only 40 years old when he died, a man who was very much loved by his family and friends, and my thoughts are with all the relatives around the world who remember their family on this day. The struggle against racism and white supremacy continues for us, let us not forget their example of courage to resist, and to fight for justice.
Program from the first wreath laying ceremony at UN Headquarters, one year after the crash, 17 September 1962:



Invitation from Acting Secretary-General, U Thant, to Madame Fabry:

Letter and commemorative UN stamps from U Thant to Olga Fabry:


Signatures from UN staff were collected from all over the world to fill this two-volume set of books in memory of Vladimir Fabry:

Signatures from UN Headquarters in New York include Ralph Bunche, and his wife Ruth:


Signatures from Geneva Headquarters and a message from John A. Olver:

Telegrams from friends in every country:

Among them, a message of sympathy from the King of Sweden relayed through Ralph Bunche:

And a cable from Jozef Lettrich:

UN cables express the loss of a dear friend and highly valued colleague:


Newspaper clippings from 1961 and 1962, the first one with a photo of Olga Fabry and her mother at the funeral in Geneva, Switzerland:








The investigation will coming up for review in the General Assembly, and for those who think we should give up and be quiet about it already after all these years, Dag Hammarskjold said it best: “Never, “for the sake of peace and quiet,” deny your own experience or convictions.”
From the family of UN officer Peter J. Hazou, I am proud to share their contribution of photos and memories from 1961, and a letter from the former Leopoldville, now Kinshasa, that was written on this day, 55 years ago.

Dag Hammarskjold, center, in white suit, his bodyguard William Ranallo at far left, and Peter J. Hazou at right in dark suit with lapel pin.
From reverse of UN photo: “SECRETARY-GENERAL LEAVES FOR CONFERENCE WITH CONGO PREMIER. UN 72653 -United Nations, Leopoldville, September, 1961. Secretary-General Dag Hammarskjold leaves UN Headquarters in Leopoldville on his way to meet Congolese Premier, Cyrille Adoula. The Secretary-General was consulting with Premier Adoula on the Katanga dispute.”

Friday, September 15, 1961
Dear Abboud and family,
We are still here in Congo and still enjoying ourselves. Peter has decided to stay a while longer as it is to our advantage financially, and so we will remain here in Congo until the end of November, 1961. At that time we are planning to take a three week cruise from Point Noir in French Congo and go up West Africa, stopping at a different port each day and ending up in Casablanca and then going to Marseille, where we will take a plane home. It will be a very interesting trip. It will get us home in cold Winter weather, though. We would stay longer but we have our house empty at home and that is a responsibility. We have registered Linda at Sacre Coeure school where they speak only French. She doesn’t know any yet but will learn quickly. In two months she won’t speak it perfectly but it will be better than nothing.
Sunday we all went on another boat ride up the Congo River. We stopped at a few islands and on one was a small African village. The children were interested in seeing how the people live. It was on the French Congo side. It is fun to go on these sandy islands. People swim from there but we don’t because the Congo River is brown and has strong currents which would pull one downstream quickly. Someone saw a crocodile once but we never did.
I take the children to the pool often because they love it. Linda swims a bit now, and Petey uses the tube. Tennis is available but I haven’t been able to get Peter to play much. He is still gaining weight but this week he intends to go on a diet. Linda has gotten very tall, and Petey is maturing nicely. I am happy that you are all well. We received your letter and it was good to get all your news. It is good Marcos is still globe-trotting, and I am glad it has been a good tourist season. I hope the weather remains pleasant for you. Over here it is still pleasantly cool, and we have rainy days now and then. The heavy rains will be coming soon and also the warm weather. Yesterday I taught our house boy to cook stuffed cabbage and Peter loved it. Also, I cook spaghetti occasionally because the family loves it. Sunday nights we sit at the outdoor gelateria and have Italian ice cream. Sometimes we go to the football matches (the Nigerians are good players) and sometimes we go to the movies, and so the time goes. There are still many cocktail parties, and the enclosed picture was taken at an Indian Officers’ one under a huge tent.
Wednesday [13 September 1961], Dag [Hammarskjold] came in and Peter was the protocol officer for the government at the airport. He greeted Adoula, Gizenga, Mobutu and Momboko[?-TB] when they arrived and then he made all the arrangements. When the S-G’s plane arrived he went up to meet him with Linner and Gen.[McKeown]. The Congolese and Nigerian bands played and it was a very nice welcome.

Tonight we will attend a big reception given by the Sec. General. This is a very crucial week here in the Congo. There is heavy fighting in Katanga, and at the huge UN army base. Last night the planes of UN personnel arrived from there as they were evacuated for safety. Don’t worry about us, though, as we are quite safe in Leopoldville as the fighting is far away. Peter is taking care of settling the refugees comfortably. If there is any big job Peter is asked to do it because they know it will get done properly. Because of this, Peter is working hard and practically running the big UN operation here but feels he doesn’t get the appreciation he deserves from headquarters, who do not realize he is working so hard because some of the other men are not capable of handling their jobs and so it falls on Peter. But it is a satisfaction to handle jobs well. He set up the whole Lovanium operation, which was tremendous and cost a million dollars. He used to have a private radio connection with it when it was locked in session, although he was one of the few people who had complete access to it. Too bad he didn’t take pictures there. We all hope the Katanga situation resolves itself quickly without civil war breaking out.
Well, Linda will start school Monday and we are glad about it. Tomorrow we will take a trip across the river to Brazzaville and look the town over. It is much smaller than Leopoldville. The past few days were warm and the hot season is starting to come in. It isn’t uncomfortable yet, though. I guess it is getting cooler in Bethlehem and the tourists are fewer. It is amazing to think that we will be having another great trip next Summer and will be with you again. I guess we can never complain about the United Nations! The children send kisses to each one of you and they are constantly drawing pictures which they say are for you. They are too bulky to send, though. Take good care of yourselves and keep in good spirits and health.
Love, Winnie
[At end of letter, Peter Hazou writes in pen:]
Dear Abboud,
I am sorry I have not been able to write more often since I have not been able to find the time. Thank you for your letters which arrive here via New York much quicker than in the past. As soon as we return to New York (about 17 December 1961) I shall resume a more regular correspondence. I am tired but healthy and I am sure the boat trip from the Congo to Marseille will do me a lot of good. My love to Mother, Victoria, Jamil and Mary and of course to yourself. I shall take a few days off and will write you a more detailed letter. The S-G will return to New York after tomorrow. The news from Katanga this evening is quite bad. I hope things improve. Love, Peter


Boat rides on the Congo River, Peter Hazou and family, 1961

Peter Hazou, Congo, 1961

First page of Lovanium Operation report from Hazou, who did tremendous work to organize all the details for the Lovanium conference to happen, dated 23 August 1961, with photo and ONUC Lovanium pass. Hazou worked for the United Nations for over three decades, from 1947 until 1978.

Peter and Winnie Hazou at left, with Sergeant Harold Julien second from right. This is likely the photo of the Indian Officer’s cocktail party mentioned in the letter, it is undated. The son of Winnie Hazou recalls: “She told me that she told Harry [Julien] at the reception how very lucky he was to be going on the mission to Katanga with the S-G”.

Hazou with unidentified person, possibly at same Indian Officer’s Party.

Invitation to the reception for Dag Hammarskjold, at La Deviniere, 15 September 1961

At reception for Hammarskjold, on the terrace at La Deviniere, Peter and Winnie with unidentified person.

La Deviniere terrace, Peter and Winnie Hazou, Joseph Kasa-Vubu, and S. Habib Ahmed

Here is the reverse of the last photo, which is dated in arabic 16 September 1961. Though she writes in the letter to Abboud that the reception for Hammarskjold was on the 15th, Winnie Hazou told her family later on that the reception was the night before the flight, the 16th, which also contradicts the date on the invitation, but the days leading up to the flight were intense with fighting, so it’s very possible that the date was moved at the last minute.

Prime Minister Cyrille Adoula, far left, with Peter Hazou on right, at Ndjili airport, Leopoldville, to transfer the 16 fallen to the Pan-Am plane.

Leopoldville, Pan-Am transport of fallen
The son of Peter and Winnie was only four years old at the time of the crash, but he remembers how he heard the news about Hammarskjold. He was at a luncheon for wives of diplomats with his mother, when the news came that Hammarskjold’s plane was announced missing, and the luncheon ended abruptly. He knew that something was wrong when his father came home in the middle of the day, which was very unusual for him. And then he saw his parents crying together. When the bodies of the fallen arrived in Leopoldville, he was on the observation deck at Ndjili airport with his family, and still recalls the intense sadness and solemnity of the people around him.
It took many people to run the United Nations Operation in the Congo, and I am glad to pay tribute to the memory of a colleague of Vlado, who no doubt grieved his death as well.

Today, my thoughts return to the status of the Hammarskjold investigation, and to all the relatives around the world who are waiting for the truth to unfold. Last week, on November 19, the United Nations General Assembly adopted by consensus the resolution which “urges all member states…to release any relevant records in their possession and to provide to the Secretary-General relevant information related to the death of Dag Hammarskjold.”
There were 74 co-sponsors to the resolution, including Zambia, Slovakia, the Czech Republic, Sweden, Haiti, South Africa, Ireland, Canada, Belgium, Germany, and France. Every nationality of those who died in 1961 has been represented, with one very notable exception: The United States. It is for this very reason I write today, I will not be silent in my support, because American citizens died for peace, and they and Vlado deserve the respect of their country.
In a statement made by Swedish Ambassador Olof Skoog, who introduced the resolution to the President of the UN General Assembly, he said “The pursuit of bringing clarity to the circumstances of the incident is particularly important to the families of all 16 victims – some of whom are present today – but also to the UN as an organization and it should remain so also for all of us as we try to come together to continue the work left unfinished by his premature death.”
It was a little more than a year ago that I was first contacted by one of the relatives, who has been instrumental in gathering us all over the world, and uniting us together to send group letters and emails to UN members in support of this investigation. Many have also written personally to UN members and heads of state to make our appeal, myself included, and I am thankful to those who were kind to respond. It gave me a lot of hope to receive a letter in reply from Swedish State Secretary for Foreign Affairs Annika Soder, dated November 20, 2014, the day after the new Swedish Government decided to take the initiative to table the resolution to support the Hammarskjold investigation.
What has not been fully appreciated by the public, and is not being reported in the news anywhere, is the quiet, behind-the-scenes efforts of all the relatives that have united for justice, and who have been paying close attention to the progress of the investigation. It’s not just my family and a handful of others that are speaking up – there are a total 105 relatives that are committed in standing together in support, so we cannot be dismissed as just a few conspiracy theorists. There are relatives to represent every person who died in the crash, with the only exception being Alice Lalande of Canada; though many people, not only the relatives, did all they could to find family that could speak up on her behalf.
I haven’t written much about the investigation recently, but I want to express today how extremely proud I am to belong to this group of dedicated and courageous people, and to be able to give them my support here, it is truly an honor.
From the family archive, here is the program from the United Nations memorial service for Secretary-General Dag Hammarskjold, and the 15 others who died with him, on 17 September 1961, while on a peace mission to Ndola. As the anniversary nears, I send kind thoughts to all who have been touched by this event. Included in the memorial program, held on 28 September 1961, is an address by the late Secretary-General Dag Hammarskjold “on the occasion of the United Nations Day Concert, 24 October 1960” – it is one of Hammarskjold’s shorter speeches, but full of his warmth and optimism for humanity, so I have transcribed it here.
To further appreciate Hammarskjold’s sentiment towards music, to feel a little of what he felt when he listened to Beethoven, I have included the Christmas Day 1989 Berlin performance of Beethoven’s Ninth Symphony, conducted by Leonard Bernstein, in celebration of the fall of the Berlin Wall – it is perfection, one of the most beautiful and moving concerts of all time.
IN MEMORIAM, 17 SEPTEMBER 1961
Dag Hammarskjold
Per Hallonquist
H.A. Wieschhoff
Nils-Eric Aahreus
Vladimir Fabry
Lars Litton
William Ranallo
Nils Goran Wilhelmsson
Alice Lalande
Harald Noork
Harold M. Julien
Karl Erik Rosen
Serge L. Barrau
S.O. Hjelte
Francis Eivers
P.E. Persson
28 SEPTEMBER 1961
“ADDRESS GIVEN BY THE SECRETARY-GENERAL ON THE OCCASION OF THE UNITED NATIONS DAY CONCERT, 24 OCTOBER, 1960”
It is the tradition that the Organization marks United Nations Day with a concert including the final movement of Beethoven’s Ninth Symphony. Today we shall, for the first time in this hall, listen to the symphony in its entirety.
It is difficult to say anything, knowing that the words spoken will be followed by this enormous confession of faith in the victorious human spirit and in human brotherhood, a confession valid for all times and with a depth and wealth of expression never surpassed.
When the Ninth Symphony opens we enter a drama full of harsh conflict and dark threats. But the composer leads us on, and in the beginning of the last movement we hear again the various themes repeated, now as a bridge toward a final synthesis. A moment of silence and a new theme is introduced, the theme of reconciliation and joy in reconciliation. A human voice is raised in rejection of all that has preceded and we enter the dreamt kingdom of peace. New voices join the first and mix in a jubilant assertion of life and all that it gives us when we meet it, joined in faith and human solidarity.
On his road from conflict and emotion to reconciliation in this final hymn of praise, Beethoven has given us a confession and a credo which we, who work within and for this Organization, may well make our own. We take part in the continuous fight between conflicting interests and ideologies which so far has marked the history of mankind, but we may never lose our faith that the first movements one day will be followed by the fourth movement. In that faith we strive to bring order and purity into chaos and anarchy. Inspired by that faith we try to impose the laws of the human mind and of the integrity of the human will on the dramatic evolution in which we are all engaged and in which we all carry our responsibility.
The road of Beethoven in his Ninth Symphony is also the road followed by the authors of the Preamble and of the Charter. It begins with the recognition of the threat under which we all live, speaking as it does of the need to save succeeding generations from the scourge of war which has brought untold sorrow to mankind. It moves on to a reaffirmation of faith in the dignity and worth of the human person, and it ends with the promise to practice tolerance and live together in peace with one another as good neighbours and to unite our strength to maintain peace.
This year, the fifteenth in the life of the Organization, is putting it to new tests. Experience has shown how far we are from the end which inspired the Charter. We are indeed still in the first movements. But no matter how deep the shadows may be, how sharp the conflicts, how tense the mistrust reflected in this hall and in this house, we are not permitted to forget that we have too much in common, too great a sharing of interests and too much that we might lose together, for ourselves and for succeeding generations, ever to weaken in our efforts to surmount the difficulties and not to turn the simple human values, which are our common heritage, into the firm foundation on which we may unite our strength and live together in peace.

IN TRIBUTE
The entire staff of the United Nations mourns the sudden and tragic death of the Secretary-General, Dag Hammarskjold, and our other colleagues who lost their lives in the service of the United Nations: Heinrich A. Wieschhoff, Vladimir Fabry, William Ranallo, Alice Lalande, Harold M. Julien, Serge L. Barrau and Francis Eivers.
Our deep sense of shock and grief on hearing of their passing is all the deeper because we knew and respected them as colleagues; because we knew, admired and shared, each in his or her own way, their devotion to the ideals of the United Nations. The entire staff of the Organization extends sincere condolences to their families in their sadness.
R.V. Klein, Chairman, Staff Committee
IN THIS HOUSE
During these somber days, many of us have known a feeling of unreality. The world’s tragedy is to us a most grievous personal loss, not easy to speak of and not easy to accept.
Never before has this house been so full of quiet sadness and never before have we had so little to say to each other.
At the bleak opening of the General Assembly we began to realize, as perhaps we had not before, how much of our identity as members of the Secretariat was found in Mr. Hammarskjold, head of this house.
Sometimes thankful for the work which has had to be done, sometimes unable to do it, we have struggled to persuade ourselves that the routine jobs are not so irrelevant and unimportant as they now seem, knowing quite well that the best way we can pay tribute to those who died is to draw strength from their example and carry on as usual–better than usual.
——————————————————————————————–
Captain Per Hallonquist
Captain Nils-Eric Aarhreus
2nd Pilot Lars Litton
Flight Engineer Nils Goran Wilhelmsson
Air Purser Harald Noork
Radio Operator Karl Erik Rosen
and
Warrant Officer S.O. Hjelte
Private P.E. Persson
These six members of the air crew and the two soldiers of the Swedish 11th Infantry Battalion serving with the ONUC were members of the Secretary-General’s team on his last flight. Their death is part of our great loss and we include their families, their friends and their countrymen in our thoughts.
We who labor “in this house” share with the whole of humanity the deep feeling of unbelief that our great and esteemed chief has been lost to us and to the world. He served humanity in the noble mission of peace and reconciliation as Secretary-General of the United Nations for eight years, five months and one week. His passing marks the close of an era of unparalleled richness — in the charting of new paths in diplomacy, in combining rare gifts of energy, wisdom and intelligence to bring crises under control and to promote programs for human betterment. Sometimes his methods had the charm and quality of a symphony; sometimes the decisive abruptness of the hammer on the anvil, but they were always calculated to gain high ends of which he never lost sight. If he had accomplished less, his epitaph might be that in opening up bold new vistas of international cooperation he belonged to a generation yet unborn. But his accomplishments are myriad–they are like snowflakes on a dotted landscape and the glistening white on the mountain peaks–countless small almost unnoticed achievements joined with decisively constructive results on great issues which only he could achieve by virtue of his office and of the rare natural gifts with which he was endowed. He belongs to our generation; he has carved his name in granite upon it; but he belongs equally to those who will come after us, benefiting by the lights he lit that can illumine their way.
He was both actor and interpreter; both history-maker and historian; with the Charter as his guide and resolutions as his directives, he mobilized and conducted the action with the scope and initiative that each situation required; his executive actions were an interpretation of the Charter which, together with his speeches and reports, gave the document a living quality of rich potentiality for the welfare of mankind.
His unflinching courage rested upon faith and his faith upon principles and ideals derived from a sturdy and valued heritage and an intellect alive with almost limitless appraisal of values with meaning for himself and humanity.
From that day–April 10, 1953–when he took his oath of office, his dedication to the task and his single-minded devotion to duty has inspired the staff and the wider world.
Although working often from dawn to midnight or in crises around the clock, he had time for wide cultural interests — in literature, drama, art and music — which were a source of constant pleasure to his associates in the United Nations family and an inspiration to the masters in these fields.
His deep inner stillness was a mainspring of his strength — a fortress so strong that disappointments, failures, setbacks and even personal attacks could not weaken his will or compromise his resolution to carry on his great task. His interest in the Meditation Room was a deeply personal one, not only aesthetic. He wrote the words on the entrance — “This is a room devoted to peace and those who are giving their lives for peace. It is a room of quiet where only thoughts should speak.” He went there frequently for quiet reflection, knowing that retreats into loneliness were a source of strength for the struggle.
Our sorrow and grief for the one who led and inspired us, extend equally to all those who died with him. In life, Heinz, Vladimir, Bill, Alive, Harry, Serge and Francis were selfless in their interests, devoted to their tasks and dedicated to the noble cause of peace which the United Nations represents. Along with him they will be hallowed in precious memory. In future it will be said of them that they died with their chief in the line of duty.
Let us not be ashamed to shed some tears over our loss, nor shrink from reflection of the void that has been created for us and the world, but let this be a part of our rededication to the task which he so nobly advanced. His concern for the staff marked by two visits to all of our offices, and in countless other ways must now be matched by our increased concern for the future of the United Nations. His greatest concern would be that the staff should carry on with new resolve and in a spirit of magnificent cooperation. Our greatest tribute to him will be our continuing individual and collective efforts, by following his glorious example, to strengthen the edifice of peace.
His words taken from the pamphlet that he wrote for visitors to the Meditation Room, now have a prophetic meaning, a charge from him to all of us: “It is for those who come here to fill the void with what they find in their center of stillness.”
— Andrew Cordier

The Secretary-General
In Memoriam
There are many, I am sure, who knew him longer. I would claim, however, that there cannot be many who could have admired and respected him more.
He was, to all appearance, cold, aloof and remote. And yet I have seen him time and again show a compassion for human frailty and an understanding of human foibles which made him more human than anyone could have guessed.
Flattery angered him. And yet, when some of his colleagues showed an understanding of the subtlety of his ways, he was genuinely pleased.
Subtle he was–so subtle that one sometimes wondered what he meant when he said something. And he never said a foolish word.
He was one of nature’s aristocrats–with a contempt for anything that was a sham or in the least shoddy or second rate.
He had a mind which could grasp a complicated problem at one go; at the same time he had a mastery of detail which was phenomenal.
His hospitality knew no limits. He was generous and forgiving, even to a fault.
In the pursuit of his goals he was clear headed and quick, sometimes seemingly too quick. But then, in this pursuit, while his speed was tempered by his political judgement, he never allowed expediency to slow him down or give him second thoughts.
He was a tireless worker. His stamina was truly astonishing. It was difficult for most of his colleagues even to keep up with him.
He made a unique contribution to the theory of internationalism. In this regard, the Introduction to the Annual Report, every word of which he wrote himself, may well be regarded as his last Will and Testament.
He died, as he lived in the last eight years and more, in quest of peace.
His death, so sudden and so cruel, is a tragic loss not only to the United Nations whose prestige he raised to such heights, but to the entire world.
—C. V. Narasimhan
Almost everyone in the Secretariat knew Bill and many of us had the privilege of working with him. Probably no other member of the staff had so many warm friends. And every one of us remembers some act of kindness, of thoughtfulness, of genuine friendship that Bill rendered for us without fanfare of any sort, readily and cheerfully.
As I write this I am wearing a pair of glasses with a very peculiar frame, one side of it held together with a screw. My frame broke last Thursday. There was no time to go to an optician. Bill undertook to fix it then and there, and although he was preparing to leave on his trip with the Secretary-General, he insisted on doing it, because he said it would not be safe to drive home at night with a broken frame.
So many of us will remember him not in generalities but in a multitude of similar acts of thoughtfulness. The son of one of our colleagues will remember him as the man who fixed his toys. Others will remember his sound practical advice on what to do, whom to see, where to go, how to cope with a difficult problem. Many a staff member will remember him for the interest he took when they were in trouble and the discreet and tactful way in which he helped. Bill made it his job to be open and sensitive to the needs of all his colleagues.
William J. Ranallo was born on February 21, 1922, in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. He worked at the Sperry Gyroscope Plant at Lake Success and from 1942 to 1946 served in the United States Army. One of his assignments was as chauffeur and guard at the estate of President Roosevelt at Hyde Park. In March 1946 he joined the Secretariat.
At first Bill was assigned as personal chauffeur to the Secretary-General. Because of his outstanding personal qualities, his efficiency, his thoroughness, his devotion to his duties and his complete dependability, Mr. Lie appointed him as his Personal Aide.
Mr. Hammarskjold gave him still larger responsibilities, particularly in connexion with security arrangements for the Secretary-General both at Headquarters and on his numerous trips. He accompanied the Secretary-General on all his missions and he grew in stature with his job. He had a rare quality of fitting in perfectly into all sorts of unusual situations. He was easily at home at formal receptions, with heads of State and other top officials of Member Governments, among security officers in the various capitals, among civilian colleagues and among the Field Service staff on UN missions.
He met people face to face, directly, straight-forwardly, with a delicately balanced combination of due regard for their official position and genuine interest in them as human beings. And this is why he was never at a loss for something interesting to say to them, or to contribute, at the right moment, to the general talk. His good humour was never-failing. It was a part of the energy and personal warmth he brought to his job. Above all, he was wholly dedicated to his task, that of assisting his chief, the man who bore so heavy a burden of history, in all the thousands of daily arrangements, to guard him against petty annoyances and irritations, and above all to guard his life.
To Bill’s father and mother, Mr. and Mrs. N. Ranallo, his wife, Eleanor, his son, Richard and his step-sons, Richard A. Gaal and William H. Gaal, the members of the Secretariat extend their deepest sympathy.
HEINRICH A. WIESCHHOFF
Heinrich A. Wieschhoff was Director and Deputy to the Under-Secretary, Department of Political and Security Council Affairs. He joined the United Nations Secretariat in 1946 with a most distinguished record of African studies behind him, both at the University of Pennsylvania and with the United States Government, and spent fourteen years in the Department of Trusteeship where he rose from consultant to Director. Called upon to organize research surveys on Trust Territories, he soon was playing an increasingly important role in all aspects of Trusteeship affairs. He was one of the leaders among the group of officials who built up the Department and helped to guide it in its far-flung activities until it can now look forward to the completion of its mission under the Charter.
His unequaled experience and wide contacts with African political leaders led him to be called upon increasingly with regard to the political problems that would arise for the United Nations in connexion with the accession of many African colonies to independent Statehood. It was therefore natural that the Secretary-General should turn to him in connexion with African affairs as that continent, with its many problems, burst into the forefront of world politics. He accompanied Mr. Hammarskjold on most of his trip through Africa in the winter of 1960. Subsequently, he was appointed Director of the Department of Political and Security Council Affairs.
Mr. Wieschhoff became one of the Secretary-General’s most intimate political advisers on Africa, assisting in the formulation of Congo policies and other African questions in regard to which political responsibilities devolved upon the the Secretary-General.
Mr. Wieschhoff was wholly devoted to the United Nations and to the cause of peace. He had a brilliantly sharp and penetrating mind which he applied not only to the analysis of political processes, but also to creative political action in conformity with the purposes and principles of the Charter.
He was a scholar, a man subject to the discipline involved in the pursuit of truth in the way of the scholar. The scholar’s discipline is sometimes stern and this was typical of Wieschhoff. He was an exacting taskmaster, particularly towards himself. He was always on guard against any kind of falsity or pretense. This at times caused him to be falsely judged as cynical. Those who knew him well saw beneath the gruff exterior, the man of high principle and lofty ideals. Many of us who were fortunate enough to enjoy his personal friendship will never forget his charm and kindness.
He worked a regular seven-day and seven-evening week, seldom took more than a few days’ leave, yet always maintained his dynamism, his good spirits, and his ability to act creatively and purposefully for the cause of peace. He was a leader among men, a valued and respected chief, and to many, a dear friend.
His untimely death has left a tragic void in the Secretariat, but especially in a closely knit family. In their hour of anguish, Virginia Wieschhoff and their three children, Heinrich, Eugenia and Virginia, know that the rich heritage which he has left them cannot be erased even by death.
Throughout her many years with the United Nations, most of them spent in the field, Alice never allowed hard work, physical hardship, or personal danger disturb her serene conviction that the job at hand must be done: now and well.
To those who worked with her, she will remain a source of inspiration as the devoted, self-possessed and unobtrusively efficient colleague that she was. For her many friends, the memory of a delicate, understanding and warm human being lives on. Who could forget her quiet smile, her ready response to a witty remark, the gay sparkle in her eyes?
Alice traveled the world in service of the United Nations. As secretary to Count Folke Bernadotte, UN Mediator in Palestine, she was on the Island of Rhodes and the borders of Syria and Lebanon when the armistice agreements were signed in 1948. She worked in Palestine for General Riley, UNTSO Chief of Staff, and for his successor, General Vagn Bennike. At the first and second UN International Conferences on the Peaceful Uses of Atomic Energy in Geneva, Alice was secretary to Professor Whitman, the first Secretary-General, and to Dr. Eklund, the second. She also served with the Department of Economic and Social Affairs at Headquarters, at UNESCO in Paris, and as an Administrative Assistant with the Preparatory Commission and first General Conference of the International Atomic Energy Agency in Vienna.
Alice is also remembered with warm affection in Gaza where she was secretary to Brigadier-General Rikhye, UNEF Chief of Staff, and in the Congo where she worked first for Ambassador Dayal and later for Dr. Sture Linner, Officer-in-Charge of the UN Operation in the Congo. While on duty in the Congo she accompanied Mr. Hammarskjold on one of his trips to South Africa.
We all share her family’s deep sense of bereavement. To those who were so dear to Alice–her father, her sister, Annette, and her brother, Abbé Lalande — goes our heartfelt sympathy in a loss which is also ours.
Dr. Vladimir Fabry, who spent almost all of his professional life in devoted and active service for the United Nations, combined to an unusual degree intellectual and physical vigor with personal charm and warmth.
When, in 1946 at the age of 25, he came to the United Nations, he held a Doctorate in Law and Political Science from the Slovak University and had completed graduate studies in Economics at the University of Bratislava; he had served in the Czech resistance movement during German occupation, had taken part in organizing the new Czech Government in liberated areas, and had been the Executive Assistant to the Minister of Commerce.
His adaptability, sound judgement and capacity for hard work made him a singularly valuable officer for mission duty, and his assignment were many and of ever-increasing responsibility. Among these were his two years’ service as Legal Affairs Officer with the Security Council’s Committee of Good Offices in the Indonesian Question in 1948, service on the UN Plebiscite in Togoland under UK administration and his particularly responsible and successful work in the Suez Canal Clearance operations for which he was commended by General Wheeler, the Secretary-General’s special representative. His service as Legal and Political Adviser with UNEF in the Middle East was, early this year, cut short by his being sent to Léopoldville as Legal Adviser with the UN Operations in the Congo, in which capacity he was accompanying the Secretary-General to Ndola on 18 September.
To his more difficult tasks Dr. Fabry brought the disciplined energy, courage, and careful preparation characteristic of a serious mountain climber–which, in fact, he was.
An enthusiastic sportsman — expert skier and horseman as well as mountaineer — Dr. Fabry was concerned to share these interests and, far from scorning the beginners or less agile among his friends and co-workers, encouraged them. He himself frequently enjoyed a solitary climb to his office on the thirty-fourth floor, a feat discovered by a colleague who, after seeing him emerge from a staircase door, jokingly asked whether he had walked upstairs and was answered with a quick smile and “yes”.
The loss of a man of such buoyant spirit, serious purpose and personal warmth leaves his colleagues and and friends sadly bereft. They share and sympathize with the great sorrow of Mrs. Fabry, his mother, and his sister, Olga.
SERGE L. BARRAU
Serge Barrau joined the UN Field Service only four months ago and was immediately assigned to service with the UN Operation in the Congo. We at Headquarters did not have the privilege of knowing him, but his friend from childhood, Serge Beaulieu of the Field Operations Service, has given us this portrait of him:
[Translated from French-T.B.]
Serge and I were childhood friends. In Port-au-Prince, his parents lived on the Rue Capois, which was the meeting place for all young people and very often the point of departure for the creation of all kinds of clubs, literary, sports and worldly. When it came to cultural events, sports or worldly, it was safe to rely of the presence and collaboration of Serge.
Strong-muscled, medium-sized, always a little smile drawn with languorous eyes under an imposing profile, he was loved by all. He had a passion for physical fitness. In football, which was also one of his favorite sports, he had the physical superiority which resulted in making him a feared and competent player. Above all, Serge Barrau was an intelligent element that could boast to have belonged to the true conscious intellectual youth of Haiti.
In spite of all these qualities and advantages, Serge was modest. He had tact, discipline in ideas, logic, which made him the arbiter in all discussions.
Separated after our studies, we met again in May this year on mission for the United Nations Organization, in Léopoldville. We had so much to say on that day. He told me about his activities in New York, his stay in the US Army where he performed his military service, his travels in Asia, particularly in Japan, where he received the baptism of fire, during a particularly dangerous drive, of moving crawling under machine gun fire, wherein the slightest imprudence can cost you your life; this training, he told me, this is my pass to the Congo. He was happy to be at the UN, to see me and to know Africa, the Africa of our ancestors.
It did not take long to prove his abilities in the UN Security Office where, newly arrived, he was assigned as assistant-investigator responsible for protecting the United Nations staff in trouble with the police.
Serge did not talk much, he did not trust himself to everyone, but he had an ideal, he wanted the initials of his name to be an example of courage and virtue to youth entire. That’s why I take pleasure in repeating his phrase which has become a reality.
S.B. – Serge Barrau – Servir bien
All his friends and colleagues express deep sympathy to Serge’s mother and father, Mr. and Mrs. Joseph Barrau, and to his brothers and sisters in their great loss.
When Harry Julien left the United States Marine Corps and joined the UN Security Force in 1952 he felt that he had found a new opportunity for service, one to be looked upon as a “great challenge”. He never lost this attitude towards his job, though he seldom spoke of it. It was in this spirit that he accepted a years’ assignment to the Spinelli Mission in Jordan in 1958 and to the Congo Mission in July of last year.
He was an active man with wide interests, among which the Marine Corps stood high. The saying “once a Marine always a Marine” was particularly true of him. He was an enthusiastic athlete, a fine swimmer and diver.
From choice he became an “outside man” on the Guard Force and so a familiar figure on First Avenue to all of us. Familiar too, in the Staff Council, was his determination that the Guard Force should be “the best it could be”; to this idea he was dedicated. He had a warm interest in other people and a very human approach which made him exceedingly good at his job. He thought little of personal comfort and, whatever the weather or his hours of duty, he was always the same, a man of natural good humour and kindliness with a cheerful smile.
In losing him, we all share the sorrow of his mother and father, his widow, Maria, and his sons, Michael and Richard.
FRANCIS EIVERS
Frank Eivers, an unassuming, soft-spoken Irishman from Bally Bay and the Dublin Police Force, joined the UN Field Service in 1956. Those who worked with him during the four years he served with UNTSO in Jerusalem and the year he served in the UN Mission in the Congo speak with admiration of his outer gentleness and inner strength, “a thread of steel”, which made him into a man who met crisis with calm, personal hardship with philosophical humour, and the need of a friend with generous and utterly reliable friendship.
Frank was a methodical man–with a whimsical sense of fun. He was a keen player of Gaelic football and endowed with extraordinary physical grace. He was also a splendid cook and his friends say with affection that only an Irish imagination could have invented some of his ways with fish.
He is remembered, too, for a most loyal devotion to his job; for many small, unselfish acts of kindness to his colleagues, and for the quiet “God bless” with which he closed every conversation.
Frank was married only one month ago, and it is with great personal sadness that we express our heartfelt sympathy to his widow, Marie, to his mother and father and sisters in the loss which we share.

A MESSAGE FROM THE PRESIDENT OF THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY
The Sixteenth Session of the General Assembly met last week in the shadow of tragedy, stricken by profound grief at the death of Mr. Hammarskjold and those members of the staff who died with him in the service of the United Nations.
Not in this Organization only, but in every corner of the troubled world, men now mourn his death because by dint of unceasing labour and selfless devotion he had come in himself to embody the ideals of the United Nations.
For all of us the task is heavier and the road darker without his courage and wisdom and without the devotion of his companions in death.
Shock and grief have shaken us to the heart, yet we must not permit them to weaken our resolve. The world pays its heartfelt tribute of grief, in which we join: but for those who had the honour of working closely with him, and especially the Secretariat, to whom his example was a perpetual inspiration, there is granted the privilege of offering a more fitting homage. It is to be rededicated to the unfinished work he and his companions had so far nobly advanced. This of all tributes is the one he would have most honouored and desired.
Let us, therefore, resolve to be worthy of the vocation to which we are called. Let his own words, addressed on the eve of his final mission, to the Secretariat in which he took such pride, and which he had sought to model in the image of his high view of its destiny, become the watchword for the future. Let all “maintain their professional pride, their sense of purpose, and their confidence in the higher destiny of the Organization itself, by keeping to the highest standards of personal integrity in their conduct as international civil servants and in the quality of the work that they turn out on behalf of the Organization”.
His death will not be the pointless and cruel calamity it now seems if everyone now stunned by grief determines to bend every effort to strengthen the United Nations as an instrument of peace.
As President of the General Assembly I can ask nothing more of the Secretariat than that with his example fresh in your minds you should resolve to set your feet firmly on the hard but rewarding path marked out by his wisdom and high purpose. I am confident that you will do so.
—Mongi Slim
From the estate of Vladimir Fabry, here are a few items of interest. First, the “Notice of Death” from Ndola, Northern Rhodesia:
(click images to enlarge)
The same notice would have been sent to the families of the other crash victims, who should be remembered here for their sacrifice:
H. A. Wieschoff
William Ranallo
Alice Lalande
Harold M. Julien
Serge L. Barrau
Francis Eivers
Per Hallonquist
Nils-Eric Aahreus
Lars Litton
Nils Goran Wilhelmsson
Harald Noork
Karl Erik Rosen
S.O. Hjelte
P.E. Persson
The post mortem of Vlado says his body was badly burned, and that he was identified by a monogrammed signet ring, so it was surprising to find this letter, and to learn I was in possession of at least one artifact from the crash:

November 9, 1961
ESTATE OF VLADIMIR FABRYMemorandum re contents of a sealed package delivered by Geneva Headquarters of United Nations to Miss Olga I. Fabry on October , 1961.
The box was tied with brown cord and the cord sealed with a metal U.N. seal. Attached to the box was an envelope from the United Nations Organization in the Congo marked “Urgent, Confidential”, addressed to Mr. John Olver of the the European office of the United Nations in Geneva. The envelope was marked “If Mr. Olver is absent, to be opened by Mr. A. Marx, Chief of Personnel.”
On opening the envelope it was found to contain a letter marked “Confidential”, dated September 29, 1961 addressed to Mr. Olver and signed by Mr. B. Grunzweig. The letter concerned the estate of the late Dr. Vladimir Fabry and stated that the writer understood that the package contained partially destroyed or burned money, travellers’ checks and notebooks belonging to Dr. Fabry. It was requested that the package be delivered to Dr. Fabry’s family, since it might be possible to recover some of the money contained therein. A copy of the letter is attached hereto.
On breaking the seal and opening the package, it was found to contain an envelope in which the following documents and currency were enclosed, all party burned and in the case of some of the currency, badly burned and difficult to decipher. The badly burned currency was in a separate envelope. On the top of the package of burned currency there appeared to be a partially burned folded bill on which the letters “llars” appeared. From what could be seen of the bill, it appeared to be U.S. currency, the denomination unknown. The bills in this package are compacted and stuck together, and they are badly burned. For that reason no attempt was made to separate these bills in order that the same in their present condition might be presented to the proper U.S. officials for examination.
The other contents of the envelope are the following:
1. A number of identification cards of the late Dr. Fabry.
2. American Express travellers’ checks partially burned on one side although readily decipherable, consisting of seven checks of $20 each bearing serial numbers Z35-790-419/425.
3. U.S. currency partially burned along one side but decipherable, consisting of 3 $10 bills and 5 $1 bills.
4. 2 Swiss 20 franc notes, partially burned along one side but readily decipherable.
5. 3 Belgian franc notes in denominations of 20, 50 and 100, respectively.
6. One singed blank airmail envelope.
7. One St. Bernard’s medal.
Though I have looked, I have found no sign of the burned notebooks. Here is all that remains from the crash, from the last moments of Vlado’s life, one St. Bernard’s medal, which I now carry as my own good luck charm: